Global Agriculture Supply Chain Management Market Size, Share, Trends 2034

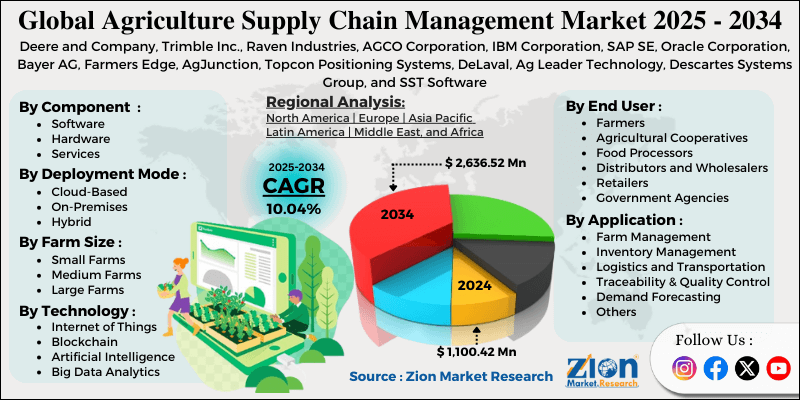
Agriculture Supply Chain Management Market By Component (Software, Hardware, Services), By Deployment Mode (Cloud-Based, On-Premises, Hybrid), By Technology (Internet of Things, Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence, Big Data Analytics, RFID and Sensors, and Others), By Application (Farm Management, Inventory Management, Logistics and Transportation, Traceability and Quality Control, Demand Forecasting, and Others), By Farm Size (Small Farms, Medium Farms, Large Farms), By End-User (Farmers, Agricultural Cooperatives, Food Processors, Distributors and Wholesalers, Retailers, Government Agencies), and By Region - Global and Regional Industry Overview, Market Intelligence, Comprehensive Analysis, Historical Data, and Forecasts 2025 - 2034
| Market Size in 2024 | Market Forecast in 2034 | CAGR (in %) | Base Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD 1,100.42 Million | USD 2,636.52 Million | 10.04% | 2024 |
Agriculture Supply Chain Management Industry Prospective
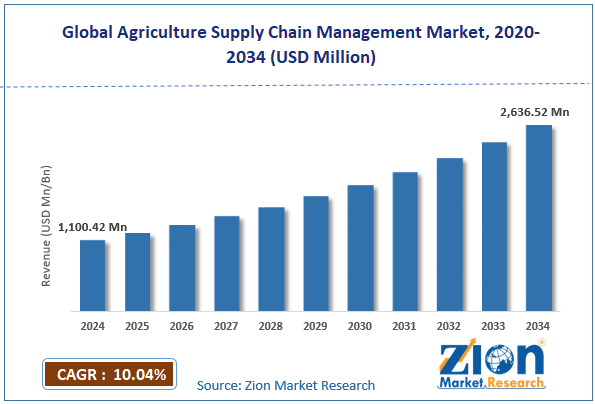
The global agriculture supply chain management market size was worth approximately USD 1,100.42 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to around USD 2,636.52 million by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 10.04% between 2025 and 2034.
Key Insights
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global agriculture supply chain management market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 10.04% over the forecast period (2025-2034).
- In terms of revenue, the global agriculture supply chain management market size was valued at approximately USD 1,100.42 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 2,636.52 million by 2034.
- The agriculture supply chain management market is projected to grow significantly due to rising food safety concerns, increasing adoption of smart farming technologies, growing need for waste reduction, expanding e-commerce food delivery, and rising demand for farm-to-table traceability.
- Based on component, the software segment is expected to lead the agriculture supply chain management market, while the services segment is anticipated to experience significant growth.
- Based on deployment mode, the cloud-based segment is expected to lead the agriculture supply chain management market, while the hybrid segment is anticipated to witness notable growth.
- Based on technology, the Internet of Things segment is the dominating segment, while the blockchain segment is projected to witness sizeable revenue over the forecast period.
- Based on application, the farm management segment is expected to lead the market compared to the traceability and quality control segment.
- Based on farm size, the large farms segment is expected to lead the market during the forecast period.
- Based on the end-user, the farmers segment is expected to lead compared to the food processors segment.
- Based on region, North America is projected to dominate the global agriculture supply chain management market during the estimated period, followed by Europe.
Agriculture Supply Chain Management Market: Overview
Agriculture supply chain management is the organized process of controlling the movement of food products from farms to consumers using technology and structured systems. It connects farmers, processors, transporters, retailers, and buyers through digital platforms that share live information on crops, storage, transport, and market demand. Sensors are used to track soil moisture, temperature, and crop health, helping farmers make better decisions on watering and harvesting. Blockchain maintains transparent records of food movement, helping consumers verify product origin and safety. Artificial intelligence analyzes data to predict crop output, market demand, and pricing trends. Farm software supports planting plans, equipment care, worker management, and cost control.
Inventory systems track perishable goods in storage and transport to reduce spoilage. Logistics platforms manage truck availability, delivery routes, and shipment tracking. Quality systems check size, ripeness, and defects. These systems support food safety, reduce losses, and improve trust across the food supply network. The growing focus on food safety and the increasing demand for supply chain transparency are expected to drive growth in the agriculture supply chain management market throughout the forecast period.
Agriculture Supply Chain Management Market Dynamics
Growth Drivers
Food safety regulations and consumer transparency demands
The agriculture supply chain management market grows fast as governments apply strict food safety rules and shoppers seek clear details on food origin and production. Food contamination causes illness and deaths, pushing regulators to demand strong tracking systems to find problem sources within hours using digital records. Many countries require complete traceability from planting through retail sales, which increases demand for digital platforms to manage farm and food records. Organic and sustainable certifications require detailed documentation of farming practices, which makes manual record-keeping more labor-intensive than automated digital data collection. Shoppers scan QR codes on food packages to see the farm source, harvest date, transport path, and quality checks for better trust. Restaurant chains and grocery stores audit suppliers to protect brand image, so farms share digital safety and quality records for approval. Export trade depends on electronic health certificates and origin proof, which makes supply chain systems necessary for the smooth international food movement.
How are the rising adoption of smart farming technologies and precision agriculture proving to be major growth factors?
The global agriculture supply chain management industry shows strong growth as farmers use connected devices and data-based decisions to raise yields and reduce waste. Precision farming employs GPS-guided machines to place seeds at appropriate depth and spacing and to apply fertilizer only where crops require support. Drones capture clear crop images across large fields to spot disease, pest activity, and water stress before losses spread across farms. Local weather stations share short-range forecasts, helping farmers choose safe planting and harvest periods and avoid frost, heat stress, and rain delays. Automated irrigation systems adjust water flow using soil moisture readings and forecast data to save water and support steady plant growth. Equipment sensors record tractor use, fuel use, and service needs to prevent breakdowns during the planting and harvest periods, thereby reducing the risk of high costs. Livestock systems track animal health, feeding patterns, and breeding cycles, and send alerts for illness care and better herd productivity planning.
Restraints
High implementation costs and technical complexity
The agriculture supply chain management market faces challenges, as high technology costs and complex systems slow adoption among small farmers with limited income and low technical experience. Early spending on sensors, drones, GPS tools, and monitoring devices becomes very expensive even before software charges and setup costs are added. Small family farms with thin profit margins find it hard to afford these systems, even when their future value and long-term benefits look promising. Ongoing software subscription fees place constant pressure on farm budgets already affected by changing crop prices and unpredictable weather conditions. Training needs require farmers to learn digital tools and computer systems, which reduces time for field work and creates stress for older workers. Poor internet access in rural areas interrupts smooth use of cloud platforms and real-time monitoring tools needed for proper farm planning. Compatibility problems arise when new digital systems must connect with old farm machines from different brands and model years. Long payback periods and fast technology changes lower farmer confidence and delay buying decisions due to fear of quick system replacement.
Opportunities
How are growing direct-to-consumer and farm-to-table movements creating opportunities in the global agriculture supply chain management market?
The agriculture supply chain management industry gains strong opportunities as more people buy food directly from farmers through local markets, farm subscription plans, and online food ordering platforms. Farmers' markets support direct selling without middlemen and need simple systems for stock tracking, payment handling, and customer management across weekly sales events. Community farm subscription programs link buyers with farms and need tools for packing boxes, planning deliveries, and sharing weekly harvest updates. Online farm stores help rural farmers reach city customers and need sales platforms connected to farm systems that provide real-time harvest quantity updates. Food delivery services work with nearby farms to provide fresh produce quickly and require livestock tracking and smooth order coordination. Restaurant partnerships create steady demand for farmers who supply seasonal food and require planning systems for order forecasting, delivery scheduling, and food quality monitoring. Local food hubs collect produce from many small farms and need advanced logistics to manage transport to schools, hospitals, and community buyers.
Challenges
How is addressing data security and farmer privacy concerns challenging for the agriculture supply chain management market?
The agriculture supply chain management market faces data safety concerns as farm operations yield records and financial details move through connected digital systems. Farm data carries business value such as crop choices, planting methods, harvest results, and buyer contacts, which farmers prefer to keep private from competitors. Technology companies that collect farm data may use these insights for product design, marketing, or data sharing without clear farmer consent. Data leaks can expose payment records, land ownership details, and work practices to criminals seeking to commit theft or gain an unfair business advantage. Data ownership issues grow between farmers who generate information and digital platforms that store, manage, and control farm records. Privacy worries increase when constant digital tracking shows daily decisions, work habits, and farm problems that owners prefer to keep confidential. Government system access raises fear of tighter control, fines, or future policy actions based on digital farm records. Cyber threats, data-sharing risks, and low trust impede adoption, as farmers fear that shared data may weaken market power and pricing control.
Agriculture Supply Chain Management Market : Report Scope
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Agriculture Supply Chain Management Market Research Report |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1,100.42 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 2,636.52 Million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 10.04% |
| Number of Pages | 220 |
| Key Companies Covered | Deere and Company, Trimble Inc., Raven Industries, AGCO Corporation, IBM Corporation, SAP SE, Oracle Corporation, Bayer AG, Farmers Edge, AgJunction, Topcon Positioning Systems, DeLaval, Ag Leader Technology, Descartes Systems Group, and SST Software |
| Segments Covered | By Component, By Deployment Mode, By Technology, By Application, By Farm Size, By End User And By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, The Middle East and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2025 - 2034 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Agriculture Supply Chain Management Market: Segmentation
The global agriculture supply chain management market is segmented based on component, deployment mode, technology, application, farm size, end-user, and region.
Based on component, the agriculture supply chain management market is divided into software, hardware, and services. Software leads the market due to its central role in data processing and decision support, lower initial costs compared to hardware investments, and scalability, allowing farms to start small and expand functionality as needs and budgets grow.
Based on deployment mode, the industry is classified into cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid. Cloud-based leads the market due to lower upfront costs without server purchases, automatic updates and maintenance handled by providers, and accessibility from any internet-connected device, enabling mobile farm management.
Based on technology, the agriculture supply chain management industry is segregated into Internet of Things, blockchain, artificial intelligence, big data analytics, RFID and sensors, and others. The Internet of Things is expected to lead the market during the forecast period due to widespread sensor-based applications that monitor crops, equipment, and environmental conditions, providing real-time data that enables responsive farm management decisions.
Based on application, the market is segmented into farm management, inventory management, logistics and transportation, traceability and quality control, demand forecasting, and others. Farm management holds the largest market share due to its comprehensive functionality, covering planting through harvest; its direct impact on farm productivity and profitability; and its fundamental importance to agricultural operations relative to downstream supply chain activities.
Based on farm size, the market is categorized into small farms, medium farms, and large farms. Large farms hold the largest market share due to greater financial resources for technology investments, higher production volumes justifying implementation costs, and operational complexity requiring sophisticated management systems beyond manual tracking capabilities.
Based on end-user, the market is divided into farmers, agricultural cooperatives, food processors, distributors and wholesalers, retailers, and government agencies. Farmers hold the largest market share due to their position at the supply chain origins, where production decisions and data generation begin; direct responsibility for crop quality and yield outcomes; and the greater number of farm operations relative to fewer downstream processors and distributors.
Agriculture Supply Chain Management Market: Regional Analysis
What factors are contributing to North America’s leading role in the global agriculture supply chain management market?
North America accounted for an estimated 38 percent market share in 2025, supported by high technology adoption, large commercial farms, and a strong focus on digital farm efficiency. North America leads the agriculture supply chain management market due to advanced digital tools, large farm sizes, and a high focus on improving daily farm productivity. The United States widely uses GPS guidance, yield sensors, and smart equipment, supporting the smooth operation of connected supply chain systems. Large farms spread across wide land areas require digital tools to manage planting, harvesting, storage, transport, labor, and cost control activities. High labor cost pushes farms to use more automation through machines, sensors, and smart systems to reduce worker load and improve output. Strong internet access across rural regions supports cloud platforms and real-time data flow between farm equipment and office systems. Food safety rules and environmental standards raise demand for proper record-keeping for inspection and quality proof.
Export activity increases the need for traceability and digital certificates for global trade. Universities, investors, and government programs together support the steady growth of digital supply chain systems across North America. Rising demand for sustainable farming practices also increases the use of digital tracking and reporting tools. Growing consumer focus on food origin transparency further supports long-term supply chain system adoption. Insurance companies and agribusiness firms also use digital data to improve risk planning and supply forecasting across the regional farm network.
Europe leads through sustainability and digital farm systems.
Europe accounted for an estimated 28 percent market share in 2025, making it the second-leading region in the agriculture supply chain management market after North America. Europe shows steady growth in agriculture supply chain management due to strict farming rules, strong sustainability focus, and high-quality food standards. European Union agricultural policies require detailed digital reports on land use, crop practices, and subsidy compliance, which increases demand for digital record systems. Strong food safety laws push farms and food companies to use complete product tracking across the supply chain. Organic farming and origin protection rules require proof of production methods and source location, which raises the use of digital verification systems.
Environmental limits on chemical use and water use encourage precision farming tools with automatic input control and reporting features. Many small farms across Europe prefer cooperative models where shared digital systems reduce cost pressures on individual farmers. European buyers value quality and origin, which increases the use of traceability tools in local and export food markets. Retailers and consumers demand sustainable food with clear proof of environmental care and ethical labor practices. Urban farming growth increases the need for tight production planning and delivery tracking inside cities. Online farm sales rules support smart logistics systems that help small producers reach customers directly. Climate change planning uses digital farm and supply chain data to adjust crops and farming methods over time.
Recent Developments
- In November 2025, AGCO presented new smart-farming and supply-chain capable equipment under brands such as Fendt and Massey Ferguson to support farms shifting toward integrated supply chain technology.
Agriculture Supply Chain Management Market: Competitive Analysis
The leading players in the global agriculture supply chain management market are
- Deere and Company
- Trimble Inc
- Raven Industries
- AGCO Corporation
- IBM Corporation
- SAP SE
- Oracle Corporation
- Bayer AG
- Farmers Edge
- AgJunction
- Topcon Positioning Systems
- DeLaval
- Ag Leader Technology
- Descartes Systems Group
- SST Software
The agriculture supply chain management market is segmented as follows:
By Component
- Software
- Hardware
- Services
By Deployment Mode
- Cloud-Based
- On-Premises
- Hybrid
By Technology
- Internet of Things
- Blockchain
- Artificial Intelligence
- Big Data Analytics
- RFID and Sensors
- Others
By Application
- Farm Management
- Inventory Management
- Logistics and Transportation
- Traceability and Quality Control
- Demand Forecasting
- Others
By Farm Size
- Small Farms
- Medium Farms
- Large Farms
By End User
- Farmers
- Agricultural Cooperatives
- Food Processors
- Distributors and Wholesalers
- Retailers
- Government Agencies
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
Table Of Content
Methodology
FrequentlyAsked Questions
HappyClients
Zion Market Research
Tel: +1 (302) 444-0166
USA/Canada Toll Free No.+1 (855) 465-4651
3rd Floor,
Mrunal Paradise, Opp Maharaja Hotel,
Pimple Gurav, Pune 411061,
Maharashtra, India
Phone No +91 7768 006 007, +91 7768 006 008
US OFFICE NO +1 (302) 444-0166
US/CAN TOLL FREE +1 (855) 465-4651
Email: sales@zionmarketresearch.com
We have secured system to process your transaction.
Our support available to help you 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Monday - Friday: 9AM - 6PM
Saturday - Sunday: Closed