Aerospace Plastic Market Size, Share, Value, Industry Trends 2034

Aerospace Plastic Market By Plastic Type (Polyetheretherketone, Polycarbonate, Polymethyl Methacrylate, Polyamide, Polyphenylene Sulfide, and Others), By Application (Interior Components, Exterior Components, Propulsion Systems, Electrical Systems, Windows and Transparencies, Structural Parts), By Aircraft Type (Commercial Aviation, Military Aviation, General Aviation, Helicopters, Space Vehicles), By Manufacturing Process (Injection Molding, Thermoforming, Compression Molding, Additive Manufacturing, Extrusion), By End-User (OEM Production, Aftermarket Replacement, Maintenance and Repair Services), and By Region - Global and Regional Industry Overview, Market Intelligence, Comprehensive Analysis, Historical Data, and Forecasts 2025 - 2034
| Market Size in 2024 | Market Forecast in 2034 | CAGR (in %) | Base Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD 14.71 Billion | USD 28.51 Billion | 7.04% | 2024 |
Aerospace Plastic Industry Perspective
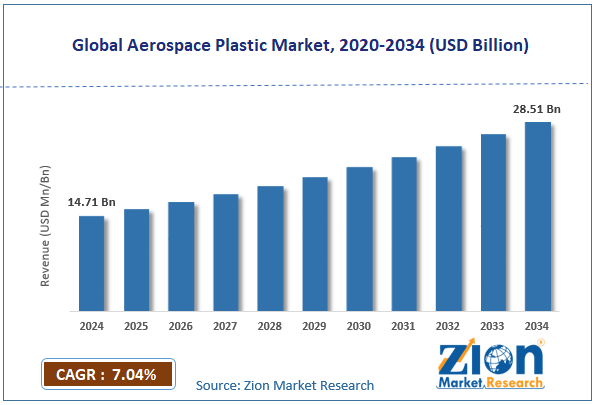
The global aerospace plastic market size was worth approximately USD 14.71 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to around USD 28.51 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 7.04% between 2025 and 2034.
Key Insights
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global aerospace plastic market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 7.04% over the forecast period (2025-2034).
- In terms of revenue, the global aerospace plastic market size was valued at approximately USD 14.71 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 28.51 billion by 2034.
- The aerospace plastic market is projected to grow significantly due to the increasing demand for lightweight aircraft materials, rising aircraft production rates globally, growing adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, and expanding applications in both interior and structural components.
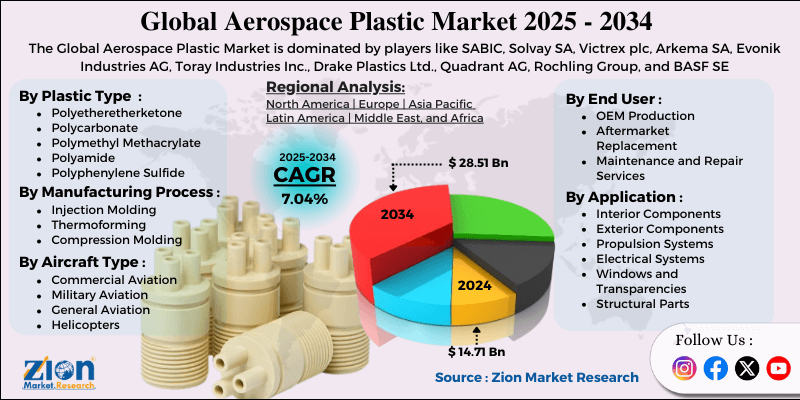
- Based on plastic type, the polyetheretherketone segment is expected to lead the aerospace plastic market, while the polyphenylene sulfide segment is anticipated to experience significant growth.
- Based on application, the interior components segment is expected to lead the aerospace plastic market, while the structural parts segment is anticipated to witness notable growth.
- Based on aircraft type, the commercial aviation segment is the dominating segment, while the space vehicles segment is projected to witness sizeable revenue over the forecast period.
- Based on the manufacturing process, the injection molding segment is expected to lead the market compared to the additive manufacturing segment.
- Based on end-user, the OEM production is expected to hold the largest market share during the forecast period.
- Based on region, North America is projected to dominate the global aerospace plastic market during the estimated period, followed by Europe.
Aerospace Plastic Market: Overview
Aerospace plastics are specialized polymer materials designed to meet the strict performance needs of aircraft and spacecraft while providing important weight savings compared with metals. These materials tolerate extreme temperature changes during flight, offer strong mechanical performance, and resist chemicals commonly used in aviation. Engineering plastics such as polyetheretherketone deliver high strength and thermal stability for parts that once required metal construction. At the same time, polycarbonate provides impact resistance and optical clarity for windows and cockpit canopies. Polymethyl methacrylate is used for lighting covers and other transparent assemblies because of its clarity and weather resistance.
Flame-retardant grades meet aviation fire safety rules by reducing fire spread and smoke generation. The low weight of these plastics improves fuel efficiency and range, and their design flexibility supports interior components, electrical insulation, and protective housings. Their durability, UV stability, and compatibility with advanced manufacturing help broaden their use as aircraft designs become more efficient. The relentless pursuit of aircraft weight reduction and the development of increasingly capable plastic materials are expected to drive growth in the aerospace plastic market throughout the forecast period.
Aerospace Plastic Market Dynamics
Growth Drivers
Environmental regulations and fuel efficiency demands
The aerospace plastic industry is growing quickly as environmental rules encourage airlines to cut carbon emissions by using lighter materials across many aircraft systems and structures. Global aviation bodies set strict emission goals, so aircraft makers focus on better fuel efficiency through steady weight reduction across new and existing fleets. Airlines also face rising fuel costs, which push them to choose lighter materials to lower long-term operating expenses over many flight cycles. Weight-reduction efforts include replacing metal parts with plastic components when performance needs allow safe, reliable material substitution in key assemblies. Each kilogram removed from an aircraft supports fuel savings across thousands of flights during its service life, creating strong financial and environmental benefits.
New aircraft designs use higher plastic content because modern plastics offer improved strength, stability, and processing advantages for various components. Airlines, governments, and defense programs support these materials to meet sustainability goals, address cost pressures, and meet performance needs across commercial, military, and business aviation.
How are the advances in high-performance plastic materials and manufacturing technologies driving the aerospace plastic market growth?
The global aerospace plastic market is growing steadily as new material innovations create plastics with strength and durability approaching metal performance in suitable aviation environments across many systems. High-temperature thermoplastics such as polyetheretherketone support demanding operating conditions and help engineers replace heavier metal components in several structural applications. Fiber-reinforced plastics combine strong fibers with lightweight matrices to deliver strength-to-weight ratios higher than common aluminum alloys used in modern aircraft designs. Additive manufacturing supports complex plastic shapes that improve performance and reduce assembly effort across various aerospace components. Thermoplastic composites offer shorter production cycles, easy repair, and useful recycling potential at the end of life for many aircraft parts. Nanotechnology improves flame resistance, stability, and mechanical behavior through the careful addition of nanoscale materials. Advanced molding methods create large plastic parts as single pieces, reducing assembly needs while supporting streamlined production. Transparent plastics reduce aircraft weight compared with glass while maintaining clarity and long-term durability across extended service periods.
Restraints
How are the material qualification challenges and conservative adoption practices limiting the aerospace plastic market growth?
The aerospace plastic market faces major challenges because every new material must undergo lengthy, costly qualification processes before gaining approval for use in certified aircraft across global aviation programs. Testing rules created by aviation authorities require detailed mechanical, thermal, and environmental assessments completed over several years before any certification decision is issued. Aircraft manufacturers also maintain internal requirements that exceed regulatory rules, so plastic suppliers must meet different expectations for each customer across various platforms. Flight testing and long service evaluations extend timelines even after laboratory results show strong performance under controlled conditions. Industry engineers often prefer older materials with long service records over newer plastics, even though newer plastics offer promising advantages in strength, durability, and stability. Certification costs reach several million dollars because suppliers must complete testing, prepare documentation, qualify production systems, and support regulatory reviews. Strict traceability rules require full documentation of raw material sources and processing steps for every batch.
Opportunities
How is the growth of electric and unmanned aircraft creating new opportunities for the aerospace plastic market?
The aerospace plastic industry is gaining strong growth opportunities as electric propulsion programs and unmanned aerial vehicle development increase demand for lightweight materials with useful electrical and thermal properties across many applications. Electric aircraft designs require aggressive weight reduction because battery systems add significant mass and influence overall flight performance across long operational cycles. Unmanned aerial vehicles produced in large quantities rely on plastic structures that support high-volume manufacturing with lower costs than traditional aerospace materials used in conventional aircraft. Battery housings and electrical enclosures in electric aircraft use flame-resistant plastics offering insulation for high-voltage systems and protection for lithium-ion cells during extended operation.
Urban air mobility vehicles under development use plastic components throughout structures and interiors to achieve meaningful weight savings and improved range across frequent short-distance flights. Delivery drones produced in very large numbers depend on injection-molded plastic airframes for efficient manufacturing. Additive manufacturing supports rapid customization for unmanned platforms, while fiber-reinforced plastics enable strong propellers and lightweight rotor blades for electric propulsion.
Challenges
Temperature limitations and environmental degradation
The aerospace plastic industry faces several obstacles because many plastic materials have limits related to temperature exposure, environmental conditions, and long-term performance reliability in demanding aviation operations. High-temperature zones near engines and exhaust systems exceed the thermal capabilities of many plastics, so engineers restrict their use to cooler aircraft areas with stable conditions. Long exposure to ultraviolet radiation during flight and ground parking causes discoloration, embrittlement, and gradual loss of strength in certain plastic components over extended service periods. Repeated temperature cycling between cold altitudes and warmer ground operations stresses plastic parts through constant expansion and contraction over many flights. Moisture absorption affects dimensional stability in humid environments, while chemical exposure creates risks when plastics contact aviation fuels and maintenance fluids. Repair procedures remain less developed than those for metal methods, and recycling difficulties add cost pressures on reinforced plastics used in modern aircraft.
Aerospace Plastic Market : Report Scope
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Aerospace Plastic Market Research Report |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 14.71 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 28.51 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 7.04% |
| Number of Pages | 220 |
| Key Companies Covered | SABIC, Solvay SA, Victrex plc, Arkema SA, Evonik Industries AG, Toray Industries Inc., Drake Plastics Ltd., Quadrant AG, Rochling Group, and BASF SE |
| Segments Covered | By Plastic Type, By Application, By Aircraft Type, By End User, By Manufacturing Process And By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, The Middle East and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2025 - 2034 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Aerospace Plastic Market: Segmentation
The global aerospace plastic market is segmented based on plastic type, application, aircraft type, manufacturing process, end-user, and region.
Based on plastic type, the global aerospace plastic industry is segregated into polyetheretherketone, polycarbonate, polymethyl methacrylate, polyamide, polyphenylene sulfide, and others. Polyetheretherketone leads the market due to its exceptional temperature resistance, enabling use in demanding applications, superior mechanical strength approaching metal performance, and excellent chemical resistance.
Based on application, the industry is segmented into interior components, exterior components, propulsion systems, electrical systems, windows and transparencies, and structural parts. Interior components lead the market due to the large number of plastic parts throughout passenger cabins and less stringent performance requirements compared to structural applications, enabling broader material choices.
Based on aircraft type, the global aerospace plastic market is classified into commercial aviation, military aviation, general aviation, helicopters, and space vehicles. Commercial aviation is expected to lead the market during the forecast period due to high aircraft production volumes and large material requirements per aircraft.
Based on manufacturing process, the global market is divided into injection molding, thermoforming, compression molding, additive manufacturing, and extrusion. Injection molding holds the largest market share due to its efficiency for high-volume production and cost-effectiveness for manufacturing small to medium-sized components in production quantities.
Based on end-user, the global market is divided into OEM production, aftermarket replacement, and maintenance and repair services. OEM production holds the largest market share due to the incorporation of plastic materials throughout new aircraft manufacturing and long-term supply agreements with aircraft manufacturers.
Aerospace Plastic Market: Regional Analysis
What factors are contributing to North America's dominance in the global aerospace plastic market?
North America leads the aerospace plastic market because major aircraft manufacturers, strong research centers, established supply chains, and advanced aviation technologies create steady demand for high-performance plastic materials across many programs. The United States hosts Boeing, along with numerous suppliers that use large volumes of plastics in commercial aircraft, military platforms, and specialized aerospace systems produced for global customers. NASA and Department of Defense funding support long-term research that develops improved plastic formulations, advanced processing methods, and reliable testing standards for future aerospace needs. Aerospace clusters in Washington, California, Texas, Kansas, and the Southeast support efficient material distribution networks and encourage collaboration across companies involved in production. Strong intellectual property protections support innovation in plastic materials, while Federal Aviation Administration certification processes offer structured approval pathways for new solutions. Business jet manufacturing centers generate demand for premium plastics used in luxury interiors, advanced displays, and durable avionics housings.
Military aircraft programs integrate lightweight materials in fighter jets, transport platforms, and unmanned systems that require strength and reliability. Additive manufacturing adoption supports complex plastic geometries for low-volume production, while university research programs enhance understanding of materials. Testing facilities provide essential infrastructure for qualification work and ongoing quality assurance across production cycles. Established supplier relationships ensure smooth communication and consistent technical support for aircraft manufacturers. Maintenance facilities across North America generate steady aftermarket demand for replacement components, while high labor costs support automation and efficient production. Canada strengthens regional capabilities through Bombardier operations and deeper supply chain participation.
Europe is experiencing significant growth.
Europe is experiencing strong growth in the aerospace plastic market because Airbus production, advanced research centers, environmental policies, and broad manufacturing capabilities create steady demand across many aviation programs. Airbus facilities in France, Germany, Spain, and the United Kingdom use large volumes of plastic materials across commercial aircraft structures, interiors, and system components. Military aviation programs, including Eurofighter, Rafael, and emerging collaborative projects, require advanced plastics that meet strict performance requirements for European defense operations. European Union research initiatives support materials development through funding programs encouraging collaboration between industry groups and university laboratories working in polymer science. Environmental regulations across Europe promote sustainable material use and encourage the development of recyclable plastic formulations suitable for long service applications. Composite manufacturing strengths in European aerospace production increase the use of plastic-matrix materials, thereby supporting the development of advanced structural components.
Business jet and regional aircraft producers rely on plastic parts for interior systems and cabin elements designed for global customers. Helicopter manufacturers, including Airbus Helicopters and Leonardo, generate ongoing demand for plastics used in specialized rotorcraft assemblies. The growing unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) industry is expanding opportunities for lightweight structures required for military and civilian missions. Space programs, including Ariane launch vehicles and satellite production, use specialized plastics suited for extreme environments. Materials research centers in Germany, France, and the United Kingdom support innovation in polymer chemistry and aerospace engineering. Automotive industry presence across Europe strengthens plastic development that transfers easily into aerospace applications. Regulatory focus on sustainability encourages the adoption of bio-based plastics across the aviation sector, while European Union supply chain integration supports efficient cross-border material distribution.
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, SABIC showcased advanced thermoplastic composite solutions at a global trade fair, emphasizing plastic materials for aircraft interiors like sidewalls, ceiling panels, overhead bins, and galley systems.
Aerospace Plastic Market: Competitive Analysis
The leading players in the global aerospace plastic market are
- SABIC
- Solvay SA
- Victrex plc
- Arkema SA
- Evonik Industries AG
- Toray Industries Inc
- Drake Plastics Ltd
- Quadrant AG
- Rochling Group
- and BASF SE
The global aerospace plastic market is segmented as follows:
By Plastic Type
- Polyetheretherketone
- Polycarbonate
- Polymethyl Methacrylate
- Polyamide
- Polyphenylene Sulfide
- Others
By Application
- Interior Components
- Exterior Components
- Propulsion Systems
- Electrical Systems
- Windows and Transparencies
- Structural Parts
By Aircraft Type
- Commercial Aviation
- Military Aviation
- General Aviation
- Helicopters
- Space Vehicles
By Manufacturing Process
- Injection Molding
- Thermoforming
- Compression Molding
- Additive Manufacturing
- Extrusion
By End User
- OEM Production
- Aftermarket Replacement
- Maintenance and Repair Services
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
Table Of Content
Methodology
FrequentlyAsked Questions
Which application areas will offer significant growth opportunities in the aerospace plastic market?
HappyClients
Zion Market Research
Tel: +1 (302) 444-0166
USA/Canada Toll Free No.+1 (855) 465-4651
3rd Floor,
Mrunal Paradise, Opp Maharaja Hotel,
Pimple Gurav, Pune 411061,
Maharashtra, India
Phone No +91 7768 006 007, +91 7768 006 008
US OFFICE NO +1 (302) 444-0166
US/CAN TOLL FREE +1 (855) 465-4651
Email: sales@zionmarketresearch.com
We have secured system to process your transaction.
Our support available to help you 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Monday - Friday: 9AM - 6PM
Saturday - Sunday: Closed