Bidirectional EV Charging Market Size, Share, Trends, Growth 2034

Bidirectional EV Charging Market By Technology Type (Vehicle-to-Grid, Vehicle-to-Home, Vehicle-to-Building, and Vehicle-to-Load), By Charger Type (AC Bidirectional Chargers and DC Bidirectional Chargers), By Power Rating (Less than 10 kW, 10 kW to 50 kW, and Above 50 kW), By Connector Type (CCS, CHAdeMO, Type 2, and Others), By Application (Residential, Commercial, and Industrial), By Vehicle Type (Battery Electric Vehicles and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles), By End-User (Individual Consumers, Fleet Operators, Utility Companies, and Commercial Establishments), and By Region - Global and Regional Industry Overview, Market Intelligence, Comprehensive Analysis, Historical Data, and Forecasts 2025 - 2034
| Market Size in 2024 | Market Forecast in 2034 | CAGR (in %) | Base Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD 1.40 Billion | USD 12.50 Billion | 24.80% | 2024 |
Bidirectional EV Charging Industry Perspective:
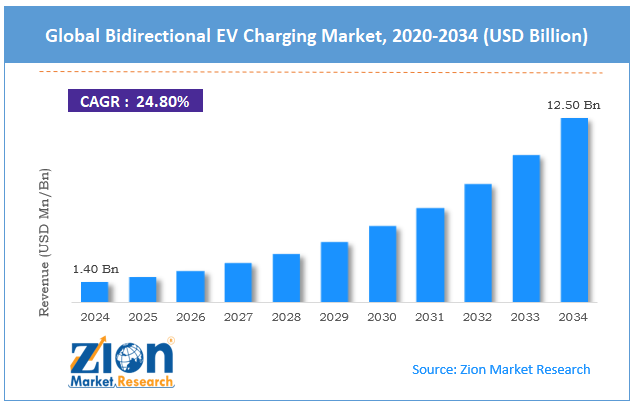
The global bidirectional EV charging market size was worth approximately USD 1.40 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to around USD 12.50 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 24.80% between 2025 and 2034.
Key Insights:
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global bidirectional EV charging market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 24.80% over the forecast period (2025-2034).
- In terms of revenue, the global bidirectional EV charging market size was valued at approximately USD 1.40 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 12.50 billion by 2034.
- The bidirectional EV charging market is projected to grow significantly due to increasing electric vehicle adoption, rising demand for energy storage solutions, growing renewable energy integration, expanding vehicle-to-grid programs, and increasing focus on grid stability and resilience.
- Based on technology type, the vehicle-to-grid segment is expected to lead the bidirectional EV charging market, while the vehicle-to-home segment is anticipated to experience significant growth.
- Based on charger type, the DC bidirectional chargers segment is expected to lead the market, while the AC bidirectional chargers segment is anticipated to witness notable growth.
- Based on power rating, the 10-kilowatt to 50-kilowatt segment is the dominating segment, while the above 50-kilowatt segment is projected to witness sizeable revenue over the forecast period.
- Based on the application, the residential segment is expected to lead the bidirectional EV charging market compared to the commercial segment.
- Based on vehicle type, the battery electric vehicles segment is expected to lead the market during the forecast period.
- Based on end-user, the utility companies segment is expected to lead compared to the individual consumers’ segment.
- Based on region, Europe is projected to dominate the global bidirectional EV charging market during the estimated period, followed by the Asia Pacific.
Bidirectional EV Charging Market: Overview
Bidirectional EV charging is a technology that lets electric vehicles both take electricity from the grid and send stored energy back to homes, buildings, or the power network. It creates a two-way flow of energy instead of the one-way flow seen in traditional charging. This allows an electric vehicle to work like a mobile battery that owners can use during power cuts, high-demand periods, or to lower electricity costs. The system uses special charging equipment and compatible vehicle features that safely manage electricity in both directions. Vehicle-to-grid systems help power companies balance demand by drawing energy from many connected vehicles, while vehicle-to-home systems provide backup power during outages. Vehicle-to-building systems help commercial spaces manage their energy use by using parked electric vehicles as temporary power sources. The chargers use smart software to track battery health, electricity prices, and grid conditions to decide when energy should flow in or out. This technology turns electric vehicles from simple transport machines into flexible energy tools that support renewable energy and improve grid stability.
The growing adoption of electric vehicles, combined with increasing energy storage needs, is expected to drive significant growth in the bidirectional EV charging market throughout the forecast period.
Bidirectional EV Charging Market Dynamics
Growth Drivers
How are the needs for integrating renewable energy driving the bidirectional EV charging market expansion?
The bidirectional EV charging market is growing quickly as utilities and energy companies explore simple ways to use solar and wind power more effectively in electrical grids. Renewable energy sources produce electricity at different levels during the day, creating difficulties for grid operators who must match supply with demand every moment. Electric vehicle batteries store extra renewable energy when production rises and release it when supplies fall, creating useful distributed storage across many vehicles. This reduces waste from solar panels during bright midday hours and wind turbines during strong night winds when demand stays low.
Grid operators prefer this flexible approach because building large battery storage sites costs far more than using vehicles already running on the roads. Vehicle owners earn money by selling stored energy during high-price periods and charging during cheaper hours. The technology supports clean energy progress by increasing renewable use and lowering dependence on fossil fuel plants during peak demand.
Growing electric vehicle adoption and battery capacity improvements
The global bidirectional EV charging market is growing quickly as electric vehicle sales rise and battery technologies offer larger storage capacities at lower costs. More automakers include bidirectional charging as a standard or optional feature, making this technology easier for regular buyers to access. Modern electric vehicles typically carry battery packs ranging from 50 kilowatt-hours to 100 kilowatt-hours, providing enough stored energy to power homes for several days during power outages. Falling battery prices make electric vehicles more affordable while increasing their usefulness as mobile power sources for homes and businesses.
Governments provide incentives for buying electric vehicles and installing bidirectional chargers, thereby lowering the initial expenses for many users. Improved battery management systems protect battery health while supporting frequent charging and discharging cycles, which are useful for grid services. Vehicle warranties cover bidirectional operation, removing worries about losing coverage when joining vehicle-to-grid programs. Charging technology improvements deliver faster power transfer and better efficiency in both directions.
Restraints
How are high initial costs and infrastructure limitations creating key restraints for the bidirectional EV charging market?
The bidirectional EV charging industry faces major challenges due to high equipment expenses and limited supporting infrastructure across many regions. Bidirectional chargers cost two to three times more than standard chargers because they use advanced power electronics and control systems to manage the safe flow of energy in both directions. Installation work adds extra expenses, as many locations require electrical panel upgrades, permits, and professional setup by certified technicians. Many homes and buildings lack the electrical capacity to support high-power bidirectional charging without costly improvements to existing wiring.
Vehicle compatibility remains restricted because only a small number of electric vehicle models support bidirectional charging, limiting adoption to specific brands and recent releases. Grid connection rules and lengthy utility approval processes create delays that discourage users from investing in these systems for regular use. Some utilities offer no payment programs for grid support, reducing clear financial benefits for vehicle owners.
Opportunities
Expansion of vehicle-to-grid programs and utility partnerships
The bidirectional EV charging market is gaining major opportunities as electric utilities create broad vehicle-to-grid programs and form partnerships with automakers and charging companies. Power companies understand millions of connected electric vehicles offer large distributed storage capacity that helps modernize aging grids without building expensive new power plants. Pilot programs in leading markets demonstrate how vehicle-to-grid systems reduce peak demand, facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, and provide backup power during natural disasters. Some regions provide special electricity rates for bidirectional charging participants, thereby increasing financial gains for many users.
Fleet operators with vans, buses, and trucks become valuable partners because these vehicles remain parked for predictable hours each day, offering steady grid support capacity. Technology companies create advanced platforms that automate bidirectional charging decisions, making participation simple while maximizing grid advantages. Regulatory changes in several countries require utilities to accept power from electric vehicles, removing barriers that previously slowed adoption. Virtual power plant models group thousands of vehicles into controllable energy resources that utilities can use like traditional power plants.
Challenges
How are standardization issues and regulatory uncertainties affecting the bidirectional EV charging market?
The bidirectional EV charging market faces major challenges linked to technical standardization and unclear regulatory rules across many regions. Several competing charging standards operate worldwide, with some supporting bidirectional capability while others do not, creating confusion for consumers and reducing equipment compatibility across brands. Vehicle manufacturers often use proprietary systems that fail to integrate smoothly with chargers from different companies, further adding to market fragmentation. Communication protocols between vehicles, chargers, and grid systems differ widely, requiring complex integration work for reliable operation. Safety standards for bidirectional use remain under development in many countries, slowing product approvals and delaying market entry for new solutions.
Insurance policies have not yet adapted to cover emerging risks associated with vehicle-to-grid activities, leaving the liability of users and service providers uncertain. Grid connection rules vary between utilities and regions, with some limiting or blocking bidirectional power flow entirely. Metering rules for tracking electricity in both directions add further cost and complexity for installers.
Bidirectional EV Charging Market: Report Scope
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Bidirectional EV Charging Market |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.40 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 12.50 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 24.80% |
| Number of Pages | 215 |
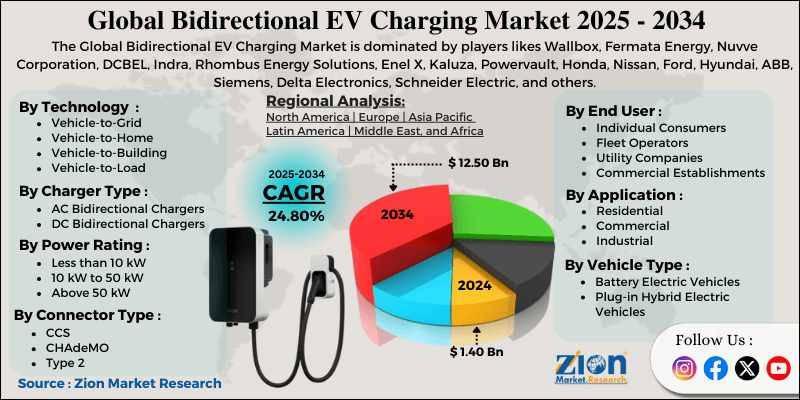
| Key Companies Covered | Wallbox, Fermata Energy, Nuvve Corporation, DCBEL, Indra, Rhombus Energy Solutions, Enel X, Kaluza, Powervault, Honda, Nissan, Ford, Hyundai, ABB, Siemens, Delta Electronics, Schneider Electric, and others. |
| Segments Covered | By Technology Type, By Charger Type, By Power Rating, By Connector Type, By Application, By Vehicle Type, By End User, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2025 - 2034 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Bidirectional EV Charging Market: Segmentation
The global bidirectional EV charging market is segmented based on technology type, charger type, power rating, connector type, application, vehicle type, end-user, and region.
Based on technology type, the global bidirectional EV charging industry is classified into vehicle-to-grid, vehicle-to-home, vehicle-to-building, and vehicle-to-load. Vehicle-to-grid leads the market due to its utility-scale applications, revenue-generating potential for users, and strong government support for grid modernization initiatives. However, vehicle-to-home is gaining traction among residential users seeking energy independence.
Based on charger type, the industry is segregated into AC bidirectional chargers and DC bidirectional chargers. DC bidirectional chargers lead the market due to their faster charging speeds, higher power delivery capacity, and suitability for commercial and utility applications where quick energy transfer is essential.
Based on power rating, the global bidirectional EV charging market is divided into less than 10 kilowatts, 10 kilowatts to 50 kilowatts, and above 50 kilowatts. The 10-kilowatt to 50-kilowatt segment is expected to lead the market during the forecast period due to its balance between performance and cost for residential and small commercial applications.
Based on connector type, the global bidirectional EV charging market is segmented into CCS, CHAdeMO, Type 2, and others. CCS holds the largest market share due to its widespread adoption by European and American automakers and its support for both AC and DC charging with bidirectional capability.
Based on application, the global market is segmented into residential, commercial, and industrial. Residential holds the largest market share due to growing homeowner interest in backup power, energy cost savings, and solar integration that bidirectional charging enables.
Based on vehicle type, the global market is segmented into battery electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Battery electric vehicles hold the largest market share due to their larger battery capacities that provide more energy storage for bidirectional applications.
Based on end-user, the global bidirectional EV charging market is segmented into individual consumers, fleet operators, utility companies, and commercial establishments. Utility companies hold the largest market share due to their active development of vehicle-to-grid programs and substantial investments in grid modernization projects.
Bidirectional EV Charging Market: Regional Analysis
Europe leads due to progressive energy policies and strong electric vehicle adoption.
Europe holds a leading position in the bidirectional EV charging market due to ambitious climate goals, supportive government policies, and high electric vehicle adoption across the region. Countries such as Germany, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and Norway use strong strategies combining electric vehicle incentives with renewable energy integration requirements. The European Union’s Green Deal and climate neutrality plans for 2050 drive major investments in clean transportation and smart grid solutions across the continent.
Many European utilities run advanced vehicle-to-grid pilot programs showing clear technical feasibility and strong economic value for long-term use. High electricity prices make energy arbitrage through bidirectional charging an appealing option for vehicle owners who can earn a profit from the price differences between charging and discharging periods. Dense urban populations and limited space for large storage sites increase the importance of distributed storage using parked electric vehicles. A strong automotive industry ensures the local production of compatible vehicles and charging equipment for expanding demand.
Renewable energy is gaining a growing share of the power generation market, thereby increasing the need for flexible storage solutions, such as those provided by electric vehicles. European standards organizations actively create interoperability rules ensuring equipment from many manufacturers works together smoothly. Consumer interest in environmental protection supports the adoption of solutions increasing renewable energy use and lowering carbon emissions across communities.
What is driving Asia Pacific's rapid growth in the bidirectional EV charging market?
Asia Pacific is experiencing rapid growth in the bidirectional EV charging market as strong electric vehicle adoption in China, Japan, and South Korea combines with urgent needs for grid stability and long-term energy security. China leads global electric vehicle sales by wide margins, creating a large potential market for bidirectional charging systems as the government promotes vehicle-to-grid integration across major regions. Japanese automakers pioneered early bidirectional charging technology and continue advancing progress through partnerships with utilities and technology companies. The region faces frequent power shortages and grid congestion, making distributed storage from electric vehicles an appealing solution for energy planners seeking reliable support. Island nations, such as Japan, value energy independence and resilience, viewing vehicle-to-grid systems as critical backup power during earthquakes and typhoons.
Government subsidies lower bidirectional charger costs significantly, helping to increase adoption across expanding markets. Smart city programs in major Asian metropolitan areas include vehicle-to-grid systems as essential parts of modern energy management plans. Growing middle-class populations raise both vehicle ownership and electricity demand at the same time. Manufacturing capabilities in China, South Korea, and Japan enable cost-efficient production of charging equipment for domestic and global markets. Regional automakers are increasingly offering bidirectional capability as standard equipment, thereby expanding the compatible vehicle population rapidly.
Recent Market Developments:
- In June 2025, Zaptec joined Octopus Energy and BYD to launch the UK’s first commercial vehicle-to-grid (V2G) bundle offering.
- In September 2025, at the IAA Mobility 2025 show, Elli (a subsidiary of Volkswagen Group) announced a pilot for bidirectional charging in private homes, enabling EV batteries to act as home storage and link with solar systems.
- In October 2025, Wallbox and Bidirectional Energy announced a multi-state pilot program in the U.S. (California & Connecticut) that uses Wallbox’s Quasar 2 bidirectional charger plus Bidirectional Energy’s virtual power-plant platform.
Bidirectional EV Charging Market: Competitive Analysis
The leading players in the global bidirectional EV charging market are:
- Wallbox
- Fermata Energy
- Nuvve Corporation
- DCBEL
- Indra
- Rhombus Energy Solutions
- Enel X
- Kaluza
- Powervault
- Honda
- Nissan
- Ford
- Hyundai
- ABB
- Siemens
- Delta Electronics
- Schneider Electric
The global bidirectional EV charging market is segmented as follows:
By Technology Type
- Vehicle-to-Grid
- Vehicle-to-Home
- Vehicle-to-Building
- Vehicle-to-Load
By Charger Type
- AC Bidirectional Chargers
- DC Bidirectional Chargers
By Power Rating
- Less than 10 kW
- 10 kW to 50 kW
- Above 50 kW
By Connector Type
- CCS
- CHAdeMO
- Type 2
- Others
By Application
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
By Vehicle Type
- Battery Electric Vehicles
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
By End User
- Individual Consumers
- Fleet Operators
- Utility Companies
- Commercial Establishments
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
Table Of Content
Methodology
FrequentlyAsked Questions
HappyClients
Zion Market Research
Tel: +1 (302) 444-0166
USA/Canada Toll Free No.+1 (855) 465-4651
3rd Floor,
Mrunal Paradise, Opp Maharaja Hotel,
Pimple Gurav, Pune 411061,
Maharashtra, India
Phone No +91 7768 006 007, +91 7768 006 008
US OFFICE NO +1 (302) 444-0166
US/CAN TOLL FREE +1 (855) 465-4651
Email: sales@zionmarketresearch.com
We have secured system to process your transaction.
Our support available to help you 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Monday - Friday: 9AM - 6PM
Saturday - Sunday: Closed