Anti Fungal Drugs Market Size, Share, Trends, Growth Analysis, & Forecasts 2034

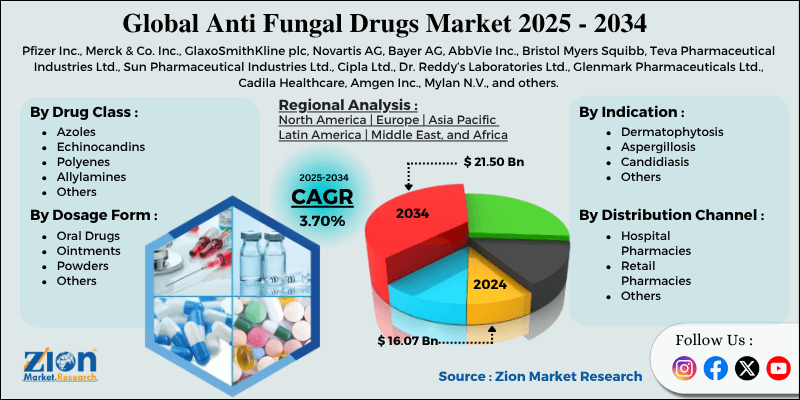
Anti Fungal Drugs Market By Drug Class (Azoles, Echinocandins, Polyenes, Allylamines, and Others), By Indication (Dermatophytosis, Aspergillosis, Candidiasis, and Others), By Dosage Form (Oral Drugs, Ointments, Powders, and Others), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, and Others), and By Region - Global and Regional Industry Overview, Market Intelligence, Comprehensive Analysis, Historical Data, and Forecasts 2025 - 2034
| Market Size in 2024 | Market Forecast in 2034 | CAGR (in %) | Base Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD 16.07 Billion | USD 21.50 Billion | 3.70% | 2024 |
Anti Fungal Drugs Industry Perspective:
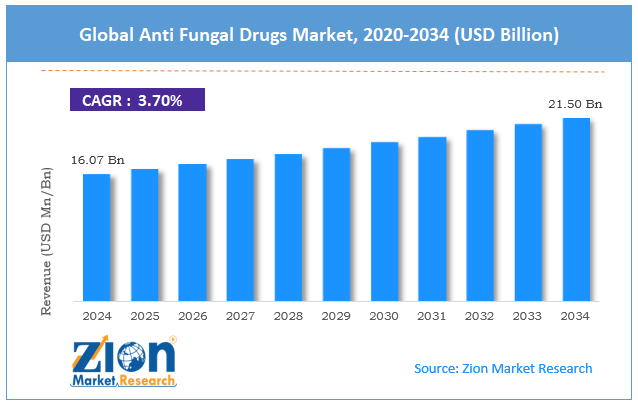
The global anti fungal drugs market size was approximately USD 16.07 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach around USD 21.50 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 3.70% between 2025 and 2034.
Anti Fungal Drugs Market: Overview
Antifungal drugs are prescribed to treat fungal infections caused by molds, yeasts, and other forms of fungi. These infections affect various parts of the body, including the nails, skin, internal organs, and respiratory system. Antifungal drugs are available in multiple forms, including oral tablets, topical creams, and intravenous solutions. The global anti fungal drugs market is poised for significant growth, driven by the increasing immunocompromised population, the broader use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, and advancements in drug formulations. Patients undergoing organ transplants, chemotherapy, and those with chronic illnesses or AIDS/HIV are more susceptible to fungal infections. More than 38 million individuals were living with HIV worldwide in 2023, according to the WHO, propelling the demand for antifungal therapeutics.
Moreover, the misuse and overuse of antibiotics disrupt the body's microbalance, leading to opportunistic fungal infections such as candidiasis. This trend eventually drives the need for effective antifungal treatment options. Innovations such as novel azoles and liposomal amphotericin B have enhanced the safety, delivery, and efficacy of antifungal drugs. These improvements expand the therapeutic landscape and motivate better patient compliance.
Nevertheless, the global market faces limitations due to factors such as adverse drug reactions and the high cost of novel therapies. Several antifungal drugs, mainly amphotericin B, are related to significant ill-effects like hepatotoxicity, allergic reactions, and nephrotoxicity, which hamper patient compliance. In addition, liposomal delivery systems and novel antifungal formulations are high-priced, thus restricting their access in developing economies. Significant production costs and R&D expenses further exacerbate this challenge.
Still, the global anti fungal drugs industry benefits from factors such as research and development (R&D) in new antifungal agents, the development of rapid diagnostics, and the growth of e-pharmacies and telemedicine. Increased investment in exploring new mechanisms of action, especially those targeting drug-resistant strains, offers key growth opportunities. The leading companies are discovering immune modulators, hybrid molecules, and peptides.
Similarly, the integration of molecular diagnostics and AI screening enables the accurate and early detection of fungal infections, leading to improved outcomes and faster treatment. Additionally, the remarkable progress of online pharmacies and telehealth post-pandemic provides a platform for enhanced access to and distribution of antifungals, particularly in remote areas.
Key Insights:
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global anti fungal drugs market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 3.70% over the forecast period (2025-2034)
- In terms of revenue, the global anti fungal drugs market size was valued at around USD 16.07 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 21.50 billion by 2034.
- The anti fungal drugs market is projected to grow significantly due to the increasing number of fungal infections, rising R&D activities for the development of antifungal drugs, and increasing adoption and awareness of antifungal drugs.
- Based on drug class, the azoles segment is expected to lead the market, while the echinocandins segment is anticipated to experience significant growth.
- Based on indication, the candidiasis segment is the largest, while the dermatophytosis segment is projected to experience substantial revenue growth over the forecast period.
- Based on dosage form, the oral drugs segment dominates, while the ointments segment is expected to experience substantial growth over the forecast period.
- Based on distribution channel, the retail pharmacies segment is expected to lead the market, followed by the hospital pharmacies segment.
- Based on region, North America is projected to dominate the global market during the estimated period, followed by Asia Pacific.
Anti Fungal Drugs Market: Growth Drivers
Rising elderly population and comorbid conditions boost market growth
The elderly population is at a higher risk of chronic illnesses and infections, including fungal diseases. According to UNDESA, more than 771 million people worldwide are 65 years of age or older, and this number is expected to exceed 1 billion by 2030. This demographic shift presents a substantial growth opportunity for antifungal therapeutics, particularly in countries such as Germany, Japan, and Italy, where the geriatric population is experiencing rapid growth.
In addition, age-associated conditions like diabetes mellitus, which compromise the immune system, create a fertile ground for fungal infections.
Improvements in delivery systems and drug formulations have remarkably fueled the market growth
The global anti fungal drugs market is advancing due to technological advancements in drug formulations and delivery mechanisms, which improve patient compliance and efficacy. New delivery systems, such as topical gels, liposomal amphotericin B, and intravenous infusion systems, offer targeted action with fewer side effects, primarily for severe systemic infections.
Latest R&D improvements include the clinical success (2024) of fosmanogepix by Pfizer, a best-in-class antifungal targeting resistant fungal strains, such as Aspergillus and Candida auris species.
Anti Fungal Drugs Market: Restraints
The limited pipeline of novel antifungal agents unfavorably impacts market progress
In comparison to cancer drugs and antibiotics, the development of the antifungal drug pipeline remains narrow, with just a handful of novel compounds entering clinical trials. The slow advancement rate is mainly because of complex fungal biology, historically restricted ROI for antifungal drugs, and significant R&D costs.
This barrier to advancement restricts the emergence of next-generation therapies, particularly amid rising resistance, thereby limiting long-term growth of the anti fungal drugs industry.
Anti Fungal Drugs Market: Opportunities
Growth of New Antifungal Drug Classes and Targets positively impacts market growth
A thrilling opportunity lies in the development of novel drug categories and pioneering antifungal agents that can combat resistant pathogens and enhance patient outcomes. Unlike earlier decades, when only three key categories—echinocandins, azoles, and polynes, led the space, the period from 2023 to 2025 has experienced a rejuvenation in research and development pipelines.
As drug resistance progresses, investors and pharmaceutical companies are increasingly drawn to advancements in antifungal treatments. With numerous candidates in late-stage experiments, a new era of antifungal therapy is emerging, presenting a promising opportunity for players in the anti fungal drugs industry, who invest in next-generation therapies.
Anti Fungal Drugs Market: Challenges
Global supply chain issues and unequal access restrict the growth of market
Global inequality in fragile supply chains and the limited availability of antifungal drugs remain key barriers to anti fungal drugs market growth. While patients in high-income countries have access to improved antifungals, such as posaconazole or liposomal amphotericin B, several vital drugs are intermittently supplied or unavailable in middle- or low-income nations. Such discrepancies limit scalability and create regional health crises, as pharmaceutical companies are hesitant to enter low-profit-margin industries without infrastructure support or government procurement guarantees.
Anti Fungal Drugs Market: Report Scope
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Anti Fungal Drugs Market |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 16.07 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 21.50 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 3.70% |
| Number of Pages | 211 |
| Key Companies Covered | Pfizer Inc., Merck & Co. Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Novartis AG, Bayer AG, AbbVie Inc., Bristol Myers Squibb, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Cipla Ltd., Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd., Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Cadila Healthcare, Amgen Inc., Mylan N.V., and others. |
| Segments Covered | By Drug Class, By Indication, By Dosage Form, By Distribution Channel, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2025 - 2034 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Anti Fungal Drugs Market: Segmentation
The global anti fungal drugs market is segmented based on drug class, indication, dosage form, distribution channel, and region.
Based on drug class, the global anti fungal drugs industry is divided into azoles, echinocandins, polyenes, allylamines, and others. The azoles segment has a substantial market share, as they are a widely prescribed drug class worldwide. This is attributed to their topical formulations, comparatively favorable safety profile, and broad-spectrum activity. Their effectiveness against Aspergillus and Candida species, combined with their affordability, contributes to their significant dominance.On the other hand, the echinocandins segment is the second-leading class, notable for their efficiency against resistant Candida strains and fewer side effects.
Based on indication, the global market is segmented into dermatophytosis, aspergillosis, candidiasis, and others. The candidiasis segment held a substantial market share owing to its high worldwide prevalence and ability to impact both systemic and superficial sites. It ranges from vaginal yeast and oral thrush infections to life-threatening invasive candidiasis in immunocompromised patients.However, the dermatophytosis segment held a fast-growing share. It comprises athlete’s foot, jock itch, and ringworm. Its higher prevalence, mainly in emerging nations, sustains strong demand for prescription and OTC antifungal drugs, contributing to its prominence.
Based on dosage form, the global anti fungal drugs market is segmented into oral drugs, ointments, powders, and others. The oral drugs segment leads the market because of their ease of administration, systemic effectiveness, and broader therapeutic coverage. Nonetheless, the ointment segment held a second-leading share, driven by the rising cases of superficial infections, such as dermophytosis, particularly in tropical climates and the APAC region.
Based on distribution channel, the global market is segmented into hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and others. The retail pharmacies segment leads the market due to OTC sales of antifungal drugs and a high volume of prescriptions. Conversely, the hospital pharmacies segment is experiencing rapid growth due to the increasing use of improved and intravenous antifungal treatments for severe infections, such as aspergillosis and candidiasis.
Anti Fungal Drugs Market: Regional Analysis
North America to witness significant growth over the forecast period
North America is projected to maintain its dominant position in the global anti fungal drugs market owing to high incidences of fungal infections, a large immunocompromised population, and an advanced healthcare ecosystem. North America, especially the U.S., reports high prevalence of both invasive and superficial fungal infections such as aspergillosis and candidiasis.
More than 75,000 cases of invasive candidiasis are reported yearly in the U.S. alone, according to the CDC, making it a leading public health concern. This consistent pressure fuels the demand for antifungal medicines in all healthcare settings. In addition, the region has a rising population of immunocompromised people, comprising AIDS/HIV patients, cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, and organ transplant recipients.
As per the CDC, more than 1.2 million individuals are living with HIV in the United States, and over 21,000 individuals were diagnosed in 2023. These categories are highly vulnerable to fungal infections, demanding ongoing antifungal treatment. North America boasts a well-developed healthcare ecosystem with modernized diagnostic and treatment facilities. The availability of superior drug formulations, such as echinocandins and amphotericin B, aids in the effective and early treatment of serious infections. Clinics and hospitals in the region routinely stock a broader range of antifungal therapies, boosting industry penetration.
The Asia Pacific maintains its position as the second-leading region in the global anti fungal drugs industry, driven by a large diabetic and immunocompromised population, rising awareness and diagnostics, and high cases of hospital-acquired infections. The region houses a speedily growing immunocompromised and diabetic population, both highly susceptible to fungal infections. For instance, India has more than 77 million diabetics, and this condition is a key factor for mucormycosis and candidiasis. This demographic inclination is propelling the demand for long-term antifungal therapies.
Furthermore, awareness of fungal diseases is increasing due to public health campaigns and post-pandemic concerns, such as the mucormycosis epidemics that have been witnessed in India. Improved diagnostics are adding to the increased use of antifungal drugs. With the growth in hospital admissions and the increasing adoption of medical devices such as ventilators and catheters, hospital-acquired fungal infections are on the rise. This leads to an increase in the use of intravenous antifungal therapies in hospitals.
Anti Fungal Drugs Market: Competitive Analysis
The leading players in the global anti fungal drugs market are:
- Pfizer Inc.
- Merck & Co. Inc.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- Novartis AG
- Bayer AG
- AbbVie Inc.
- Bristol Myers Squibb
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Cipla Ltd.
- Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd.
- Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
- Cadila Healthcare
- Amgen Inc.
- Mylan N.V.
Anti Fungal Drugs Market: Key Market Trends
Higher emphasis on novel drug formulations:
Companies are heavily investing in nanotechnology-based antifungal and liposomal formulations to reduce toxicity and enhance the delivery of drugs. For example, liposomal amphotericin B offers reduced nephrotoxicity and broadens the use in vulnerable populations.
Rising investments in fungal surveillance and diagnostics:
Global health agencies and governments are funding the development of improved surveillance systems and diagnostic tools to detect fungal infections early. Technologies like lateral flow devices, PCR assays, and fungal biomarkers are gaining prominence. Speedy and accurate diagnosis is enhancing treatment outcomes and driving the demand for antifungal drugs.
The global anti fungal drugs market is segmented as follows:
By Drug Class
- Azoles
- Echinocandins
- Polyenes
- Allylamines
- Others
By Indication
- Dermatophytosis
- Aspergillosis
- Candidiasis
- Others
By Dosage Form
- Oral Drugs
- Ointments
- Powders
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Others
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
Table Of Content
Methodology
FrequentlyAsked Questions
Antifungal drugs are prescribed to treat fungal infections caused by molds, yeasts, and other forms of fungi. These infections affect various parts of the body, including the nails, skin, internal organs, and respiratory system. Antifungal drugs are available in multiple forms, including oral tablets, topical creams, and intravenous solutions.
The global anti fungal drugs market is projected to grow due to the emergence of novel antifungal agents, the growing elderly population that is susceptible to fungal infections, and the rising immunocompromised population.
According to study, the global anti fungal drugs market size was worth around USD 16.07 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 21.50 billion by 2034.
The CAGR value of the anti fungal drugs market is expected to be approximately 3.70% from 2025 to 2034.
North America is expected to lead the global anti fungal drugs market during the forecast period.
The key players profiled in the global anti fungal drugs market include Pfizer Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Novartis AG, Bayer AG, AbbVie Inc., Bristol Myers Squibb, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Cipla Ltd., Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd., Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Cadila Healthcare, Amgen Inc., and Mylan N.V.
The report examines key aspects of the anti fungal drugs market, including a detailed analysis of existing growth factors and restraints, as well as an examination of future growth opportunities and challenges that will impact the market.
HappyClients
Zion Market Research
Tel: +1 (302) 444-0166
USA/Canada Toll Free No.+1 (855) 465-4651
3rd Floor,
Mrunal Paradise, Opp Maharaja Hotel,
Pimple Gurav, Pune 411061,
Maharashtra, India
Phone No +91 7768 006 007, +91 7768 006 008
US OFFICE NO +1 (302) 444-0166
US/CAN TOLL FREE +1 (855) 465-4651
Email: sales@zionmarketresearch.com
We have secured system to process your transaction.
Our support available to help you 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Monday - Friday: 9AM - 6PM
Saturday - Sunday: Closed