Cell Therapy Technologies Market Size, Share, Trends, Growth 2034

Cell Therapy Technologies Market By Therapy Type (Autologous and Allogeneic), By Cell Type (Stem Cells, T Cells, NK Cells, Dendritic Cells, and Others), By Technology (Gene Editing, Cell Expansion, Cell Separation and Isolation, Cryopreservation, and Others), By Application (Oncology, Cardiovascular Diseases, Orthopedic Disorders, Neurological Disorders, Immunological Disorders, and Others), By End-User (Hospitals and Clinics, Research Institutions, Biopharmaceutical Companies, and Cell Banks), and By Region - Global and Regional Industry Overview, Market Intelligence, Comprehensive Analysis, Historical Data, and Forecasts 2025 - 2034
| Market Size in 2024 | Market Forecast in 2034 | CAGR (in %) | Base Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD 6.56 Billion | USD 34.04 Billion | 17.90% | 2024 |
Cell Therapy Technologies Industry Perspective:
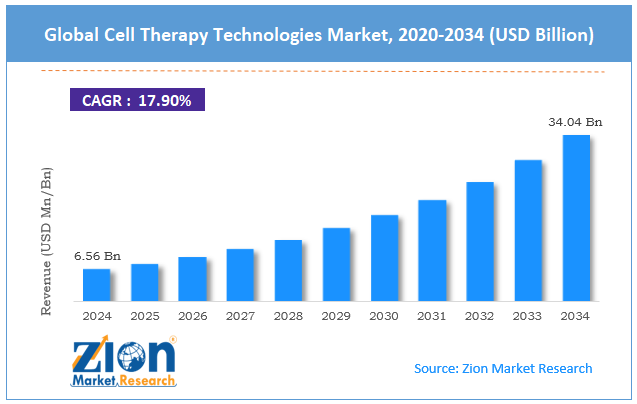
The global cell therapy technologies market size was worth approximately USD 6.56 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to around USD 34.04 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 17.90% between 2025 and 2034.
Key Insights:
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global cell therapy technologies market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 17.90% over the forecast period (2025-2034).
- In terms of revenue, the global cell therapy technologies market size was valued at approximately USD 6.56 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 34.04 billion by 2034.
- The cell therapy technologies market is projected to grow significantly due to rising cancer incidence, increasing regulatory approvals for cell-based therapies, growing investment in regenerative medicine research, expanding applications beyond oncology, technological advancements in manufacturing and gene editing, and increasing collaboration between biopharmaceutical companies and research institutions.
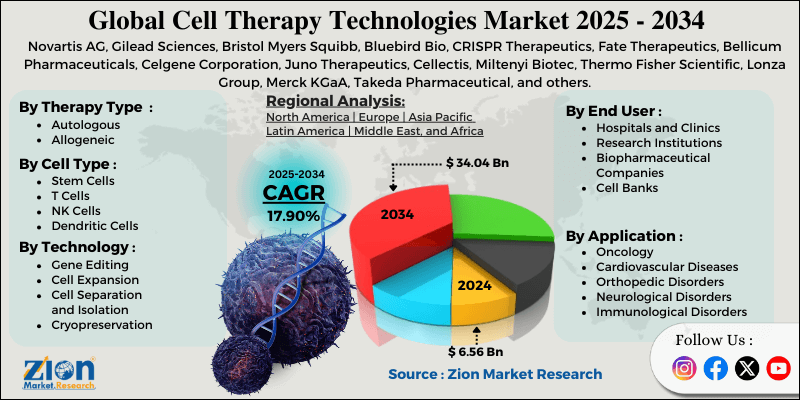
- Based on therapy type, the autologous segment is expected to lead the cell therapy technologies market, while the allogeneic segment is anticipated to experience significant growth.
- Based on cell type, the T cells segment is expected to lead the market compared to the stem cells segment.
- Based on technology, the gene editing segment is the dominating segment, while the cell expansion segment is projected to witness sizeable revenue over the forecast period.
- Based on application, the oncology segment is expected to lead the market during the forecast period.
- Based on end-user, the hospitals and clinics segment is expected to dominate compared to the research institutions segment.
- Based on region, North America is projected to dominate the global cell therapy technologies market during the estimated period, followed by Europe.
Cell Therapy Technologies Market: Overview
Cell therapy technologies refer to medical methods that use living cells to treat or prevent diseases by repairing, replacing, or regenerating damaged tissues and organs. These treatments involve collecting cells from patients or donors, growing or modifying them in controlled laboratory environments, and returning them to the body to restore healthy function. The field includes stem cell therapies that can turn into specific cell types, immune cell therapies that strengthen the body’s ability to fight cancers, and tissue engineering techniques that create biological substitutes for damaged tissues. The process generally involves collecting the required cells, isolating and purifying them, expanding their numbers in culture systems, and sometimes altering their genes to improve effectiveness.
Afterward, the cells undergo safety and quality tests, are preserved through freezing, and are prepared for treatment. Supporting technologies include automated processing systems, specialized bioreactors, gene editing tools, precise freezing equipment, and analytical instruments. Treatments may utilize a patient’s own cells or donor cells and are applied to various conditions, including cancers, genetic disorders, autoimmune diseases, and degenerative conditions.
The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing success of approved cell therapies are expected to drive growth in the cell therapy technologies market throughout the forecast period.
Cell Therapy Technologies Market Dynamics
Growth Drivers
Cancer immunotherapy successes and expanding oncology applications
The cell therapy technologies market is growing quickly as CAR-T and immune cell treatments show strong success across several difficult cancers. Blood cancers such as leukemias, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma respond very well, with many patients reaching complete remission. Researchers are expanding these therapies into solid tumors like lung, breast, and pancreatic cancer through steady scientific progress. Combination approaches using cell therapy with chemotherapy, radiation, or checkpoint inhibitors offer improved results for many patients. Personalized medicine is well-suited for autologous therapies, which are made from a patient’s own cells, allowing for precise treatment. Many relapsed patients with limited options gain new hope through advanced cellular immunotherapy programs.
Pediatric teams also use these treatments when standard methods fail or cause severe side effects. TIL therapies use immune cells taken from tumors and expanded for reinfusion, while NK cell therapies offer off-the-shelf options. Dendritic cell vaccines help the immune system recognize cancer cells more effectively. Regulatory approvals build trust in safety and effectiveness, and insurance providers are gradually offering coverage. Hospitals are creating dedicated centers with trained staff for safe delivery. Advocacy groups raise awareness and support research progress. Long-term results show durable responses not seen with traditional treatments.
How do improved manufacturing technologies and automation lower costs and accelerate growth in the cell therapy technologies market?
The global cell therapy technologies market continues to grow as new manufacturing methods make production faster, safer, and more cost-effective. Automated systems reduce manual work and lower contamination risks, while closed bioreactors keep cells in clean and well-controlled environments. Single-use parts make equipment easier to manage and prevent cross-contamination. Real-time monitoring tools enable quick adjustments during cell growth, while artificial intelligence enhances accuracy by predicting batch quality.
Mini bioreactors allow quick testing, and microfluidic devices sort specific cell types with high purity. Gene editing becomes more reliable through better delivery methods, and viral vector production scales efficiently. Cryopreservation methods protect cell function, and automated testing saves time and resources. Improved supply chains, specialized facilities, contract manufacturers, and standardized processes increase efficiency across regions. Continuous production further boosts stability and reduces delays.
Restraints
High treatment costs and reimbursement challenges
The cell therapy technologies industry faces serious challenges because of very high treatment costs, which limit patient access and put pressure on healthcare systems. Single treatments often become extremely expensive due to complex manufacturing steps and the need for intensive medical care. Insurance providers struggle to approve coverage while protecting budgets for other essential needs. Government health programs in many regions lack clear systems for evaluating and funding these costly options. Prior authorization requirements slow patient access and increase administrative burden. Cost-effectiveness reviews often show uncertain long-term value compared with standard treatments.
Hospital reimbursement models do not fully cover the high costs associated with these expenses. Risk-sharing agreements linking payment to outcomes create extra complexity for payers and manufacturers. Patient out-of-pocket costs can become overwhelming even with insurance support. Income differences raise ethical concerns about fair treatment and access. Lower-income countries cannot provide these therapies to most of their citizens. Clinical trials offer access for some patients but exclude many others. Healthcare systems prioritize treatments with stronger evidence of long-term value. Budget competition across medical areas forces difficult funding decisions.
Opportunities
How do broader applications beyond oncology open new opportunities in regenerative medicine for the cell therapy technologies market?
The cell therapy technologies industry is seeing strong opportunities as these treatments expand beyond cancer and support many common medical conditions. Cardiovascular programs use cardiac stem cells to repair heart tissue after severe heart attacks. Orthopedic teams utilize mesenchymal stem cells to aid in cartilage repair, bone healing, and the relief of osteoarthritis symptoms. Neurological research studies treatments for Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, stroke recovery, and memory disorders. Autoimmune conditions such as Crohn’s disease, lupus, and multiple sclerosis respond well to regulatory T cells that support balanced immune function. Type 1 diabetes programs develop beta cells to restore natural insulin production.
Patients with liver disease receive hepatocyte transplants that help improve organ function. Retinal cell therapies protect or restore vision in degenerative eye diseases. Wound care uses cell treatments to improve healing in burns and ulcers. Genetic disorders such as sickle cell anemia and beta-thalassemia gain promising new options. Tissue engineering creates functional structures using cells and biomaterials, also known as scaffolds. Aging research explores tissue repair, while cosmetic medicine studies cell-based skin and hair treatments.
Challenges
How are manufacturing complexity and supply chain vulnerabilities challenging the cell therapy technologies market?
The cell therapy technologies market faces major challenges in maintaining consistent manufacturing quality while managing complex supply chains built around living and highly sensitive materials. These therapies require precise control during collection, processing, and final administration to protect fragile cells from damage. Even small temperature changes during transportation can ruin entire batches and create major financial losses. Raw material variation from media ingredients, growth factors, and laboratory reagents introduces unpredictable shifts in performance.
Supplier quality issues sometimes force production delays or recalls. Patient-to-patient differences complicate the production of autologous therapies, and donor screening for allogeneic therapies requires extensive testing. Maintaining sterility during open processing steps poses contamination risks that can lead to the termination of entire production runs. Scale-up from research to commercial manufacturing exposes unexpected failures, and facility design requires strict containment systems. Quality testing delays product release, regulatory inspections require remediation, global distribution creates logistical complexity, cold chain failures threaten product integrity, and limited capacity restricts patient treatment during high-demand periods.
Cell Therapy Technologies Market: Report Scope
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Cell Therapy Technologies Market |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 6.56 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 34.04 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 17.90% |
| Number of Pages | 214 |
| Key Companies Covered | Novartis AG, Gilead Sciences, Bristol Myers Squibb, Bluebird Bio, CRISPR Therapeutics, Fate Therapeutics, Bellicum Pharmaceuticals, Celgene Corporation, Juno Therapeutics, Cellectis, Miltenyi Biotec, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Lonza Group, Merck KGaA, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and others. |
| Segments Covered | By Therapy Type, By Cell Type, By Technology, By Application, By End User, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2025 - 2034 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Cell Therapy Technologies Market: Segmentation
The global cell therapy technologies market is segmented based on therapy type, cell type, technology, application, end-user, indication, and region.
Based on therapy type, the global cell therapy technologies industry is classified into autologous and allogeneic. Autologous therapies lead the market due to currently approved product concentration in this category, reduced immunological rejection risks, regulatory pathway clarity, and established manufacturing practices despite higher costs and longer production times.
Based on cell type, the industry is segregated into stem cells, T cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, and others. T cells hold the largest market share due to the dramatic successes of CAR-T therapies in blood cancers, multiple approved products on the market, an extensive clinical pipeline, and proven mechanisms of action supported by robust clinical evidence.
Based on technology, the global cell therapy technologies market is divided into gene editing, cell expansion, cell separation and isolation, cryopreservation, and others. Gene editing is expected to lead the market during the forecast period due to its critical role in enhancing cell therapeutic properties, CRISPR technology adoption, and the ability to create next-generation therapies with improved persistence and reduced toxicity.
Based on application, the global market is segmented into oncology, cardiovascular diseases, orthopedic disorders, neurological disorders, immunological disorders, and others. Oncology holds the largest market share due to the highest number of approved therapies, the largest clinical trial pipeline, urgent unmet medical needs in cancer treatment, and demonstrated clinical efficacy, generating strong demand.
Based on end-user, the global market is segmented into hospitals and clinics, research institutions, biopharmaceutical companies, and cell banks. Hospitals and clinics hold the largest market share due to their role as treatment administration sites, which require specialized infrastructure, trained personnel, and intensive patient monitoring capabilities throughout the therapy process.
Cell Therapy Technologies Market: Regional Analysis
How is North America leading the cell therapy technologies market through its innovation ecosystem and regulatory leadership?
North America holds a leading position in the cell therapy technologies market because of world-class research institutions, a supportive regulatory environment, strong venture capital investment, and a large biopharmaceutical presence, which drive steady innovation and development. Academic medical centers run advanced clinical trials, translating early discoveries into real patient treatments. Biotechnology centers in Boston, San Francisco, and San Diego promote innovation through concentrated talent and collaborative ecosystems. Major pharmaceutical companies partner with or acquire developers, pushing the field forward. Contract manufacturing firms offer essential production capacity for growing demand.
Hospitals expand cell therapy programs and invest in infrastructure preparation. Insurance providers create coverage strategies for newly approved options. Patient advocacy groups raise research support and public awareness. Intellectual property protection strengthens long-term innovation incentives for companies. Immigration policies attract global scientific talent, improving overall capabilities. Clinical trial networks speed enrollment and support efficient data collection.
Regulatory science expertise helps teams to effectively manage complex approval requirements. Workforce training programs strengthen available manufacturing skills and capabilities. Supply chain systems support reliable temperature-controlled product distribution. Financial markets supply capital supporting high-risk therapeutic development. Media coverage increases public awareness and patient interest across the region. Academic-industry agreements enable effective technology transfer and collaborative progress.
Europe ranks second due to strong research and regulation.
Europe maintains a strong competitive position in the cell therapy technologies market because of its scientific excellence, collaborative networks, progressive regulations, and universal healthcare systems, which support steady growth across the region. Academic centers in Germany, the United Kingdom, Switzerland, and France contribute major scientific advances across many therapeutic areas. Public funding programs support translational initiatives connecting basic discoveries with clinical development. Pan-European consortia share knowledge, resources, and clinical evidence across multiple countries. Universal healthcare systems simplify clinical trial enrollment and improve post-approval patient access. Cell and gene therapy accelerators in the United Kingdom strengthen commercial translation activities. Hospital exemption rules allow earlier access to investigational treatment options when necessary.
A highly trained scientific workforce supports industry progress across research and manufacturing. Ethical guidelines strike a balance between innovation incentives and patient safety protections. Patient registries collect long-term outcome data that strengthen the clinical evidence base. Manufacturing capabilities expand through facility investments and contract organizations offering regional capacity. Cross-border collaboration enables multi-country clinical trials with broader enrollment opportunities. Public-private partnerships distribute development risks and support innovation growth. Regional manufacturing hubs serve multiple markets with efficient distribution. Reimbursement decisions at the national level determine final patient access. Scientific societies promote best practices and support standardization efforts. Venture capital and pharmaceutical investment continue to fuel ecosystem expansion.
Recent Market Developments:
- In April 2024, Johnson & Johnson and Bristol Myers Squibb were granted U.S. FDA approval for earlier-line use of their CAR-T therapies (Carvykti and Abecma) in certain multiple myeloma patients, significantly expanding the eligible patient pool.
- In May 2024, Bristol Myers Squibb received U.S. FDA accelerated approval for its CAR-T therapy Breyanzi in relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma after two or more prior systemic therapies.
- In June 2025, the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) and Miltenyi Biotec India signed a strategic collaboration to enhance local manufacturing capacity and research capabilities in the cell & gene therapy sector in India.
Cell Therapy Technologies Market: Competitive Analysis
The leading players in the global cell therapy technologies market are:
- Novartis AG
- Gilead Sciences
- Bristol Myers Squibb
- Bluebird Bio
- CRISPR Therapeutics
- Fate Therapeutics
- Bellicum Pharmaceuticals
- Celgene Corporation
- Juno Therapeutics
- Cellectis
- Miltenyi Biotec
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Lonza Group
- Merck KGaA
- Takeda Pharmaceutical
The global cell therapy technologies market is segmented as follows:
By Therapy Type
- Autologous
- Allogeneic
By Cell Type
- Stem Cells
- T Cells
- NK Cells
- Dendritic Cells
- Others
By Technology
- Gene Editing
- Cell Expansion
- Cell Separation and Isolation
- Cryopreservation
- Others
By Application
- Oncology
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Orthopedic Disorders
- Neurological Disorders
- Immunological Disorders
- Others
By End User
- Hospitals and Clinics
- Research Institutions
- Biopharmaceutical Companies
- Cell Banks
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
Table Of Content
Methodology
FrequentlyAsked Questions
HappyClients
Zion Market Research
Tel: +1 (302) 444-0166
USA/Canada Toll Free No.+1 (855) 465-4651
3rd Floor,
Mrunal Paradise, Opp Maharaja Hotel,
Pimple Gurav, Pune 411061,
Maharashtra, India
Phone No +91 7768 006 007, +91 7768 006 008
US OFFICE NO +1 (302) 444-0166
US/CAN TOLL FREE +1 (855) 465-4651
Email: sales@zionmarketresearch.com
We have secured system to process your transaction.
Our support available to help you 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Monday - Friday: 9AM - 6PM
Saturday - Sunday: Closed