Aerospace Titanium Market Size, Share, Value, Industry Report 2034

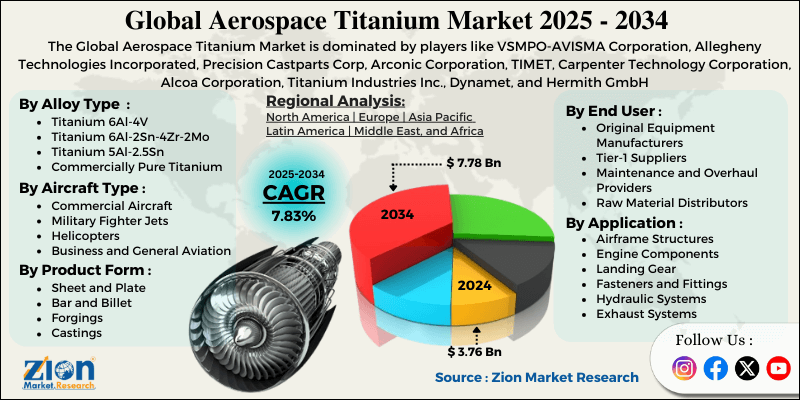
Aerospace Titanium Market By Alloy Type (Titanium 6Al-4V, Titanium 6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo, Titanium 5Al-2.5Sn, Commercially Pure Titanium, Beta Titanium Alloys, and Others), By Application (Airframe Structures, Engine Components, Landing Gear, Fasteners and Fittings, Hydraulic Systems, Exhaust Systems), By Aircraft Type (Commercial Aircraft, Military Fighter Jets, Helicopters, Business and General Aviation, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, Space Launch Vehicles), By Product Form (Sheet and Plate, Bar and Billet, Forgings, Castings, Tubing and Pipe), By End-User (Original Equipment Manufacturers, Tier-1 Suppliers, Maintenance and Overhaul Providers, Raw Material Distributors), and By Region - Global and Regional Industry Overview, Market Intelligence, Comprehensive Analysis, Historical Data, and Forecasts 2025 - 2034
| Market Size in 2024 | Market Forecast in 2034 | CAGR (in %) | Base Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD 3.76 Billion | USD 7.78 Billion | 7.83% | 2024 |
Aerospace Titanium Industry Perspective
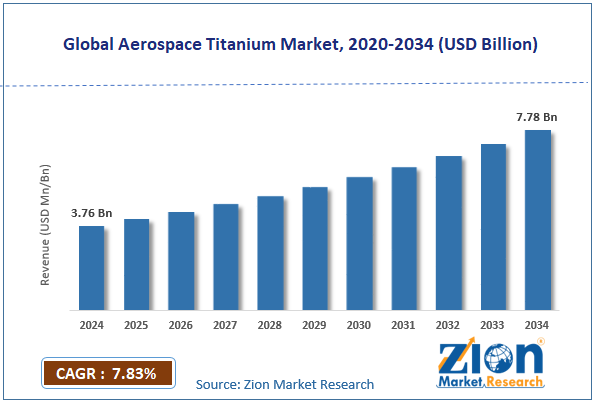
The global aerospace titanium market size was worth approximately USD 3.76 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to around USD 7.78 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 7.83% between 2025 and 2034.
Key Insights
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global aerospace titanium market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 7.83% over the forecast period (2025-2034).
- In terms of revenue, the global aerospace titanium market size was valued at approximately USD 3.76 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7.78 billion by 2034.
- The aerospace titanium market is projected to grow significantly due to the rising production of commercial aircraft with higher titanium content, increasing military aviation modernization programs, growing adoption of titanium in additive manufacturing, and expanding use in space exploration vehicles.
- Based on alloy type, the titanium 6Al-4V segment is expected to lead the aerospace titanium market, while the beta titanium alloys segment is anticipated to experience significant growth.
- Based on application, the engine components segment is expected to lead the aerospace titanium market, while the airframe structures segment is anticipated to witness notable growth.
- Based on aircraft type, the commercial aircraft segment is the dominating segment, while the space launch vehicles segment is projected to witness sizeable revenue over the forecast period.
- Based on product form, the forgings segment is expected to lead the market compared to the castings segment.
- Based on end-user, the original equipment manufacturers segment is expected to lead the market during the forecast period.
- Based on region, North America is projected to dominate the global aerospace titanium market during the estimated period, followed by Europe.
Aerospace Titanium Market: Overview
Aerospace titanium is a high-performance metal used in aircraft and spacecraft because it combines strong mechanical strength, light weight, and excellent resistance to corrosion and heat. Titanium alloys are stronger than aluminum and lighter than steel, which helps reduce overall aircraft weight and improve fuel efficiency. The material does not rust easily, so it performs well in salty, humid, and harsh environments without the need for heavy protective coatings. Titanium also maintains its strength at high temperatures, which makes it suitable for engine parts where other metals may fail. It is widely used in compressor sections, landing gear, fasteners, hydraulic components, and structural frames. Military aircraft and space vehicles depend on titanium to achieve high speed, durability, and safety under extreme conditions.
Although titanium is expensive and difficult to process, it remains essential for modern aerospace design. New aircraft models continue to increase titanium use to support lighter structures and better flight performance. Growing space missions also increase demand for titanium parts that perform reliably under extreme pressure and temperature conditions. The increasing production of next-generation commercial aircraft and growing military aviation expenditures are expected to drive growth in the aerospace titanium market throughout the forecast period.
Aerospace Titanium Market Dynamics
Growth Drivers
How are next-generation aircraft programs driving the growth of the aerospace titanium market?
The aerospace titanium market is growing rapidly as new aircraft designs use higher levels of titanium to reduce weight and improve overall performance. Modern commercial aircraft use much more titanium than older models, helping airlines save fuel while keeping strong and reliable structures. New engine designs include large titanium compressor sections built for high pressure, high heat, and long service life under heavy mechanical stress. Military aircraft programs use titanium across frames and engines to support high-speed flight, sharp maneuvering, and long missions with lower structural weight. Unmanned aircraft designs use titanium structures to carry heavier payloads, extend flight range, and remain stable during sharp turns and rapid climbs. High-speed research vehicles require titanium parts to withstand the extreme heat generated from air friction while maintaining shape, strength, and control during demanding test flights. Space systems use titanium in rockets, landers, satellites, and fuel tanks because of its weight, strength, and resistance to corrosion, enabling safe launch, use, and operation in space.
Expanding additive manufacturing applications and advanced processing techniques
The global aerospace titanium market grows steadily as additive manufacturing supports the production of complex parts that were once difficult or costly to produce using traditional manufacturing methods. Laser powder-bed and electron-beam technologies create lightweight titanium parts with internal shapes designed for strength, airflow control, and heat management. Design software places material only in load areas, creating smooth organic shapes possible only through printing, with no limits from cutting tools. Material waste has reduced greatly since printing uses near exact volumes, unlike machining, where most titanium turns into metal chips. Production time shortens, enabling printed parts to reach users faster without waiting for forging tools or long machining schedules. Aircraft manufacturers gain affordable customization, as printed titanium parts match each design need without high tooling costs. Spare part supply improves as printing supports on-demand production without holding large inventories across global aerospace service networks today. Repair methods use printed material buildup to restore worn titanium surfaces, while advanced cutting, forming, and welding reduce overall manufacturing cost levels.
Restraints
High material costs and supply chain limitations
A major challenge for the aerospace titanium market is high prices, driven by the complex extraction and processing steps required to produce usable titanium metal. Production begins with ore conversion into chemical form, followed by metal recovery using magnesium or sodium under controlled vacuum conditions. These energy-heavy steps raise overall cost and make titanium much more expensive than aluminum and steel. Limited global production capacity creates supply pressure during periods of strong aircraft demand across several large aviation programs. Titanium supply remains concentrated in only a few countries, which increases risk from trade limits and global political changes. Long lead times for forgings and complex parts often exceed one year, causing delays in aircraft production planning. Strict quality testing increases cost and time, while machining waste causes heavy loss when most purchased titanium becomes scrap. Tool wear, recycling difficulty, and lower-cost competing materials continue to limit wider titanium use across price-sensitive aerospace applications.
Opportunities
How is the commercialization of space exploration creating new opportunities for the aerospace titanium market?
The aerospace titanium industry is experiencing strong growth as space agencies and private companies expand rocket launches, satellite programs, and deep space missions needing durable titanium materials. Reusable rocket programs increase titanium demand, as structures must withstand repeated thermal, pressure, and mechanical stresses across many launch and landing cycles. Large satellite constellations require thousands of units, each built with titanium components for structural support, propulsion, and long operational life in orbit. Lunar mission programs develop landers, habitats, and rovers using titanium for safe performance in harsh surface conditions. Mars mission planning requires titanium across spacecraft frames, landing systems, and surface vehicles built for dust, cold temperatures, and long mission periods.
Space stations and commercial platforms use titanium for pressure vessels, frames, and systems exposed to radiation and wide temperature changes. Research into space manufacturing studies titanium printing in microgravity to build parts directly in orbit without an Earth supply. Space tourism vehicles, deep space probes, servicing spacecraft, and long transfer vehicles all depend on titanium for lightweight, strength, safety, and long life in extreme space conditions.
Challenges
How are manufacturing complexities and technical limitations affecting the aerospace titanium industry growth?
The aerospace titanium industry faces many production challenges because natural material behavior makes forming, cutting, and joining difficult during regular manufacturing operations. High chemical reactivity at high temperatures requires vacuum or inert gas environments, which increase equipment costs and add complexity to factory setup. Hardening during machining causes rapid tool wear and forces frequent speed control to keep cutting stable and surface finish acceptable. Low heat flow traps heat at cutting edges, causing faster tool damage and raising demand for specialized tools. Forming titanium sheets creates shape recovery after bending, so complex dies and extra forming steps are necessary. Welding requires strong gas shielding, as air contamination can cause porosity, cracks, and weak joints in finished components. Joining with other metals increases corrosion risk and requires isolation methods, special fasteners, and controlled contact during assembly operations. Inspection remains difficult due to signal loss during testing, limited cold formability, surface contamination risk, and thickness needs for stiffness in deflection-sensitive designs.
Aerospace Titanium Market : Report Scope
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Aerospace Titanium Market Research Report |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 3.76 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 7.78 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 7.83% |
| Number of Pages | 220 |
| Key Companies Covered | VSMPO-AVISMA Corporation, Allegheny Technologies Incorporated, Precision Castparts Corp, Arconic Corporation, TIMET, Carpenter Technology Corporation, Alcoa Corporation, Titanium Industries Inc., Dynamet, and Hermith GmbH |
| Segments Covered | By Alloy Type, By Application, By Aircraft Type, By Product Form, By End User And By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, The Middle East and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2025 - 2034 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Aerospace Titanium Market: Segmentation
The global aerospace titanium market is segmented based on alloy type, application, aircraft type, product form, end-user, and region.
Based on alloy type, the global aerospace titanium industry is segregated into titanium 6Al-4V, titanium 6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo, titanium 5Al-2.5Sn, commercially pure titanium, beta titanium alloys, and others. Titanium 6Al-4V leads the market due to its excellent balance of mechanical properties, good weldability and formability, and extensive qualification history with aircraft manufacturers.
Based on application, the industry is segmented into airframe structures, engine components, landing gear, fasteners and fittings, hydraulic systems, and exhaust systems. Engine components lead the market due to the critical performance requirements in high-temperature environments, and high material consumption in large turbofan engines powering commercial and military aircraft.
Based on aircraft type, the global aerospace titanium market is classified into commercial aircraft, military fighter jets, helicopters, business and general aviation, unmanned aerial vehicles, and space launch vehicles. Commercial aircraft are expected to lead the market during the forecast period due to high production volumes, substantial titanium content per aircraft in next-generation models, and strong growth in global passenger aviation driving fleet expansion.
Based on product form, the global market is divided into sheet and plate, bar and billet, forgings, castings, and tubing and pipe. Forgings hold the largest market share due to their use in critical structural applications that require superior mechanical properties and their widespread adoption in engine components and landing gear systems.
Based on end user, the global market is divided into original equipment manufacturers, tier-1 suppliers, maintenance and overhaul providers, and raw material distributors. Original equipment manufacturers hold the largest market share due to their direct consumption of titanium materials in new aircraft and engine production, and long-term supply agreements providing demand visibility.
Aerospace Titanium Market: Regional Analysis
What factors are contributing to North America's dominance in the global aerospace titanium market?
North America leads the aerospace titanium market because the region has many large aircraft makers, engine companies, space programs, and strong military support for the aviation and defense industries. The United States is home to Boeing, whose commercial and military aircraft use large volumes of titanium in airframes, engines, landing gear, and internal structural parts. Engine makers such as Pratt & Whitney, General Electric Aviation, and Honeywell use titanium in jet engines for strength, heat resistance, and weight reduction. Defense companies, including Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, rely on titanium for fighter jets, transport aircraft, and unmanned systems used in demanding military missions. The United States also has many titanium production plants that supply aerospace-grade material for forging, machining, and advanced 3D printed components. Modern factories use large forging presses, high-precision machining centers, and additive manufacturing systems to produce complex titanium parts with consistent quality.
Military budgets from the U.S. Department of Defense support steady titanium demand for new aircraft, system upgrades, and long-term fleet expansion programs. Space activities led by NASA, SpaceX, and Blue Origin also increase titanium use in rockets, spacecraft, launch vehicles, and space exploration systems designed for extreme conditions. Business jet manufacturing in Kansas and other regions adds steady demand for lightweight and high-performance aircraft used for private and corporate travel. Strong supply chains, skilled workers, research universities, testing systems, and aerospace manufacturing in Canada together strengthen North America’s leading position in the global aerospace titanium industry. This strong industry ecosystem helps the region maintain stable production, steady innovation, and long-term leadership in aerospace titanium use worldwide.
Europe is experiencing significant growth.
Europe stands as the second-leading region in the aerospace titanium market due to its strong aircraft manufacturing base, advanced engine development, and high defense and space investment across many countries. The region is home to Airbus, one of the world’s largest aircraft manufacturers, whose commercial and military aircraft use large volumes of titanium in airframes, engines, landing gear, and fasteners. Major European engine makers such as Rolls-Royce and Safran rely heavily on titanium for jet engine parts that must handle high heat and pressure. Defense programs across France, Germany, Italy, and the United Kingdom use titanium in fighter jets, transport aircraft, and unmanned systems for strength, speed, and long service life. Europe also has strong capabilities in titanium processing and machining, supporting a steady supply of aerospace-grade materials. Advanced factories across the region use forging, precision machining, and additive manufacturing to produce complex titanium components with high accuracy.
The European space sector also drives titanium demand through satellite production, launch vehicles, and deep space missions supported by the European Space Agency. Growing satellite constellations, space exploration projects, and reusable launch systems are driving demand for lightweight, durable titanium structures. Business aviation across Europe adds further demand for titanium in high-performance jets serving private and corporate travel. Strong supply chain coordination, strict quality standards, skilled labor, and close collaboration between manufacturers and research institutes support continued market stability. With ongoing investment in clean aviation, defense modernization, and space exploration, Europe is expected to remain a key growth region in the global aerospace titanium market.
Recent Developments
- In April 2025, Airbus signed an agreement to source titanium from a Saudi Arabian supplier to help reduce reliance on Russian supply after recent geopolitical disruptions.
- In November 2025, Aequs, an aerospace contract manufacturer, announced that global titanium supply constraints are “almost resolved,” as it adapts supply-chain and procurement strategies to support ongoing aerospace production.
Aerospace Titanium Market: Competitive Analysis
The leading players in the global aerospace titanium market are
- VSMPO-AVISMA Corporation
- Allegheny Technologies Incorporated
- Precision Castparts Corp
- Arconic Corporation
- TIMET
- Carpenter Technology Corporation
- Alcoa Corporation
- Titanium Industries Inc
- Dynamet
- Hermith GmbH
The global aerospace titanium market is segmented as follows:
By Alloy Type
- Titanium 6Al-4V
- Titanium 6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo
- Titanium 5Al-2.5Sn
- Commercially Pure Titanium
- Beta Titanium Alloys
- Others
By Application
- Airframe Structures
- Engine Components
- Landing Gear
- Fasteners and Fittings
- Hydraulic Systems
- Exhaust Systems
By Aircraft Type
- Commercial Aircraft
- Military Fighter Jets
- Helicopters
- Business and General Aviation
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
- Space Launch Vehicles
By Product Form
- Sheet and Plate
- Bar and Billet
- Forgings
- Castings
- Tubing and Pipe
By End User
- Original Equipment Manufacturers
- Tier-1 Suppliers
- Maintenance and Overhaul Providers
- Raw Material Distributors
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
Table Of Content
Methodology
FrequentlyAsked Questions
HappyClients
Zion Market Research
Tel: +1 (302) 444-0166
USA/Canada Toll Free No.+1 (855) 465-4651
3rd Floor,
Mrunal Paradise, Opp Maharaja Hotel,
Pimple Gurav, Pune 411061,
Maharashtra, India
Phone No +91 7768 006 007, +91 7768 006 008
US OFFICE NO +1 (302) 444-0166
US/CAN TOLL FREE +1 (855) 465-4651
Email: sales@zionmarketresearch.com
We have secured system to process your transaction.
Our support available to help you 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Monday - Friday: 9AM - 6PM
Saturday - Sunday: Closed