Global Corrosion Inhibitors Market Size, Share, Report 2034

Corrosion Inhibitors Market By Product (Organic and Inorganic), By Type (Water Based and Oil Based), By End-Use (Oil and Gas, Metal Processing, Power Generation, Chemical Processing, Water Treatment, Paper and Pulp, and Others), and By Region - Global and Regional Industry Overview, Market Intelligence, Comprehensive Analysis, Historical Data, and Forecasts 2025 - 2034
| Market Size in 2024 | Market Forecast in 2034 | CAGR (in %) | Base Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD 9.1 Billion | USD 13.2 Billion | 3.8% | 2024 |
Corrosion Inhibitors Industry Prospective:
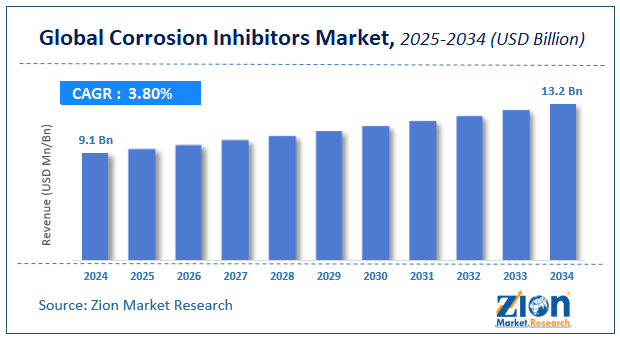
The global corrosion inhibitors market size was worth around USD 9.1 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 13.2 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 3.8% between 2025 and 2034.
Key Insights
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global corrosion inhibitors market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 3.8% over the forecast period (2025-2034).
- In terms of revenue, the global corrosion inhibitors market size was valued at around USD 9.1 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 13.2 billion by 2034.
- The increasing oil and gas industry is expected to drive the corrosion inhibitors market over the forecast period.
- Based on the product, the organic segment is expected to dominate the market over the projected period.
- Based on the type, the oil-based segment is expected to capture the largest market share over the projected period.
- Based on the end use, the oil and gas segment is expected to capture the largest market share over the projected period.
- Based on region, the Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period.
Corrosion Inhibitors Market: Overview
Corrosion inhibitors are substances that have a minimal but significant chemical impact and are added to fluids, paints, or environments to prevent or slow the corrosion of metals and alloys in contact with moisture, acids, salts, or high temperatures. Depending on the type of inhibitor used, these can either form a protective layer on the metal surface, alter the electrochemical reactions that drive corrosion, or remove corrosive agents from the system, thereby inhibiting corrosion. Corrosion inhibitors are used across multiple industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, power generation, construction, automotive, and manufacturing.
In all the above-mentioned industries, corrosion inhibitors are used to protect pipes, storage tanks, boilers, and cooling systems. Today's industrial asset protection programs are largely based on corrosion inhibitors, which prolong equipment life, provide a safer working environment, reduce repair costs, and prevent costly shutdowns. The expansion of industrial activities and major infrastructure projects worldwide is increasing the use of metals and alloys in pipelines, structural frameworks, and machinery. This heightens the need for corrosion protection solutions, thereby driving demand for corrosion inhibitors across sectors like construction, manufacturing, and utilities.
Corrosion Inhibitors Market Dynamics
Growth Drivers
How does growth in the oil & gas and energy sectors propel growth in the corrosion inhibitors industry?
As oil and gas companies grow, they create more jobs by making it necessary to find better ways to protect key infrastructure from corrosion. Pipelines, drilling equipment, storage tanks, and offshore platforms are always in situations that are hard on metal, such as high pressure, extreme temperatures, salty water, acidic gases, and dampness. As more money is spent on finding, producing, refining, and expanding pipelines, especially in offshore areas and unconventional resources, the need for corrosion inhibitors grows to preserve assets, keep operations safe, and maintain smooth production.
There are also more and more thermal, nuclear, and renewable power facilities in the energy market. Boilers, heat exchangers, cooling systems, and condensers should all be treated with corrosion inhibitors to extend their lifespan and improve performance. Corrosion inhibitors are an inexpensive and vital solution, as they reduce failures caused by corrosion, maintenance time, and repair and replacement costs. This helps the corrosion inhibitors business grow a lot.
For instance, according to Exxon Mobil Corporation, in 2024 LNG accounted for nearly 15% of global natural gas demand and is projected to increase to >20% by 2050 as global LNG demand doubles.
Restraints
Why is the increasing use of corrosion-resistant materials impeding the corrosion inhibitors industry’s growth?
The increasing use of non-corrosive materials is slowing the growth of the corrosion inhibitors industry, as it makes people less dependent on chemical corrosion inhibitors in the long run. More and more industries are using materials that resist corrosion, such as stainless steel, duplex and super-duplex alloys, customized polymers, composites, and coated metals. These materials can withstand harsh conditions such as high salinity, extreme temperatures, and harsh chemicals without requiring frequent chemical treatment. Because they require less ongoing maintenance, don't involve handling or disposal of chemicals, and last longer, end users often choose these materials even though they cost more initially. This change is especially clear in older markets and industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing, where safety and reliability are highly important. As corrosion-resistant materials replace metals that require inhibitor dosing, the overall need for corrosion inhibitors is declining, slowing the sector's expansion.
Opportunities
Will the demand from water treatment and utilities offer a potential opportunity for the corrosion inhibitors market growth?
The water treatment and utilities market, characterized by steadily rising demand, is likely to offer strong growth potential in the coming years. The water industry faces several factors that demand effective corrosion control, including the deterioration of water infrastructure, urban population growth, and investment in municipal and industrial water and wastewater treatment systems. Utilities face a variety of waste-causing factors, such as leaks, corrosion, and poor water quality, which can increase maintenance and replacement costs.
Corrosion inhibitors are considered necessary for utilities to prevent the aforementioned problems and thus extend asset life and reduce costs. Other factors that might increase the competitiveness of inhibitors include regulations on water safety and system reliability, which, in turn, push utilities to use more advanced, greener corrosion inhibitors. Thus, as global governments move towards water security and infrastructure modernization, the water treatment and utilities sector will remain the most important for the corrosion inhibitors industry.
Challenges
Limited awareness in the developing region poses a major challenge to market expansion.
One of the primary barriers to industry expansion is a lack of awareness in developing regions, as the majority of small and medium-sized industrial players do not consider the long-term effects of corrosion or the value of preventive measures. Corrosion is frequently a reactive rather than a proactive issue in some emerging economies, owing to a lack of technical knowledge, a scarcity of skilled labor, limited access to and experience with modern corrosion management practices, and financial constraints, particularly among local manufacturers and municipal utility companies.
Furthermore, decision-makers may view the initial reduced costs of traditional methods as more appealing than the long-term benefits from using corrosion inhibitors, treating the latter as an avoidable expense rather than a strategic investment. Insufficient regulatory enforcement, combined with little exposure to global best practices, is one of the issues slowing adoption. As a result, the use of corrosion inhibitors remains low in developing regions, preventing the market from expanding despite increased industrial and infrastructure activity.
Corrosion Inhibitors Market: Report Scope
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Corrosion Inhibitors Market |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 9.1 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 13.2 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 3.8% |
| Number of Pages | 280 |
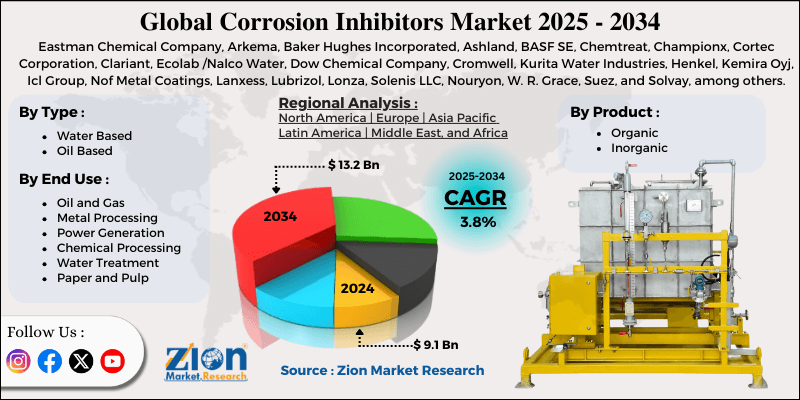
| Key Companies Covered | Eastman Chemical Company, Arkema, Baker Hughes Incorporated, Ashland, BASF SE, Chemtreat, Championx, Cortec Corporation, Clariant, Ecolab /Nalco Water, Dow Chemical Company, Cromwell, Kurita Water Industries, Henkel, Kemira Oyj, Icl Group, Nof Metal Coatings, Lanxess, Lubrizol, Lonza, Solenis LLC, Nouryon, W. R. Grace, Suez, and Solvay, among others. |
| Segments Covered | By Product, By Type, By End Use, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, The Middle East and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2025 - 2034 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Corrosion Inhibitors Market: Segmentation
Product Insights
The organic segment is expected to dominate the market, with over 75% of the revenue share. There are a number of built-in benefits and new end-use applications that are helping the category flourish. A significant number of people use organic inhibitors, such as amines, azoles, and other carbon-based compounds, because they form effective protective films on metal surfaces. This protects against corrosion across many industrial settings, including oil and gas, water treatment, automotive, and power generation. They are more flexible and desirable than many inorganic alternatives because they perform well across a wide range of metal systems and operating conditions. This means they have a larger market share and generate higher revenue.
Type Insights
The oil-based segment is expected to hold the largest revenue share of more than 55% over the projected period. These compositions are especially beneficial in heavy-duty industrial settings, as they protect metals better in tough, non-aqueous environments and in the presence of powerful corrosive chemicals. Oil-based inhibitors adhere well and repel water, making them effective at protecting metal surfaces from high temperatures, chemicals, and changing pressures. These conditions are typical in the oil and gas, petrochemical, and associated energy sectors. This performance in challenging service environments sustains high demand for oil-based products, particularly as exploration, production, and transportation infrastructure expand worldwide.
End Use Insights
The oil and gas segment is expected to hold the largest revenue share of more than 30% over the projected period. The oil and gas industry is one of the biggest and fastest-growing end-user segments in the corrosion inhibitors market. This is because global energy demand is rising and investments in oil and gas infrastructure are rising, especially for long-distance pipelines, offshore platforms, and enhanced recovery operations. There is a strong demand for corrosion control in critical energy assets, and this demand is growing. This directly supports and drives revenue development in the corrosion inhibitors market.
Corrosion Inhibitors Market: Regional Analysis
The Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the corrosion inhibitors market growth with a revenue share of 38% in 2024. Countries like China, India, Japan, and Southeast Asia are rapidly developing their cities and industries. This means that metals and industrial equipment are being used more in industries such as power generation, oil and gas, water treatment, construction, and manufacturing, all of which are highly corrosive and require effective inhibitor solutions. This large growth in industry creates greater demand for corrosion inhibitors to protect pipes, machinery, and infrastructure, which brings in more money for the region.
In addition, the Asia-Pacific region accounts for a large share of global corrosion inhibitor use due to ongoing investments in energy and utility facilities, such as power plants and refineries, where controlling corrosion is important for maintaining asset condition and operational efficiency. As utilities increasingly use chemical protection to save on maintenance and extend the life of their equipment, the region's growing water treatment facilities and infrastructure modernization projects are driving up demand for inhibitors. These factors, along with increased awareness of the benefits of corrosion control and the growth of the chemical manufacturing and distribution industry, are driving strong demand for corrosion inhibitors in the Asia-Pacific market.
Corrosion Inhibitors Market: Competitive Analysis
The global corrosion inhibitors market is dominated by players like-
- Eastman Chemical Company
- Arkema
- Baker Hughes Incorporated
- Ashland
- BASF SE
- Chemtreat
- Championx
- Cortec Corporation
- Clariant
- Ecolab /Nalco Water
- Dow Chemical Company
- Cromwell
- Kurita Water Industries
- Henkel
- Kemira Oyj
- Icl Group
- No Metal Coatings
- Lanxess
- Lubrizol
- Lonza
- Solenis LLC
- Nouryon
- W. R. Grace
- Suez
- Solvay
The global corrosion inhibitors market is segmented as follows:
By Product
- Organic
- Inorganic
By Type
- Water Based
- Oil Based
By End Use
- Oil and Gas
- Metal Processing
- Power Generation
- Chemical Processing
- Water Treatment
- Paper and Pulp
- Others
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
Table Of Content
Methodology
FrequentlyAsked Questions
HappyClients
Zion Market Research
Tel: +1 (302) 444-0166
USA/Canada Toll Free No.+1 (855) 465-4651
3rd Floor,
Mrunal Paradise, Opp Maharaja Hotel,
Pimple Gurav, Pune 411061,
Maharashtra, India
Phone No +91 7768 006 007, +91 7768 006 008
US OFFICE NO +1 (302) 444-0166
US/CAN TOLL FREE +1 (855) 465-4651
Email: sales@zionmarketresearch.com
We have secured system to process your transaction.
Our support available to help you 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Monday - Friday: 9AM - 6PM
Saturday - Sunday: Closed