Medical Radioisotopes Market Size, Share, Trends, Growth and Forecast 2034

Medical Radioisotopes Market By Type (Tc-99m, Cobalt-60, Iodine Radioisotopes), By Application (Nuclear Therapy, Equipment Radioactive Source, Diagnosis, and Others), By End-User (Hospitals, Diagnostic Centers, and Others), and By Region - Global and Regional Industry Overview, Market Intelligence, Comprehensive Analysis, Historical Data, and Forecasts 2025 - 2034
| Market Size in 2024 | Market Forecast in 2034 | CAGR (in %) | Base Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD 5.90 Billion | USD 11.00 Billion | 8.10% | 2024 |
Medical Radioisotopes Industry Perspective:
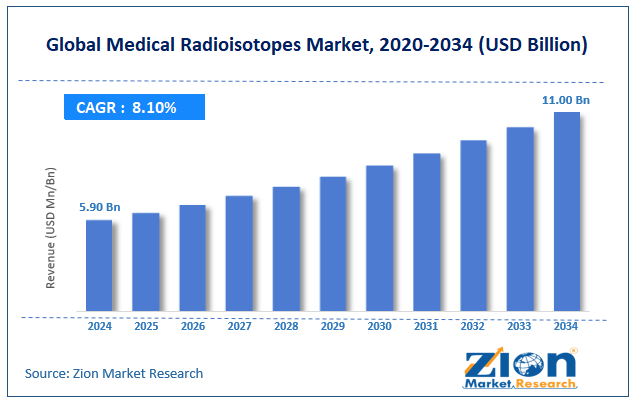
The global medical radioisotopes market size was worth around USD 5.90 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 11.00 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 8.10% between 2025 and 2034.
Medical Radioisotopes Market: Overview
Medical radioisotopes are radioactive elements used in nuclear medicine for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases. They emit radiation that visualizes internal organs using imaging methods like SPECT and PET scans.
Additionally, some radioisotopes are preferred in targeted radiotherapy to destroy cancerous cells with minimal damage to surrounding tissues. The global medical radioisotopes market is driven by the increasing incidence of cardiovascular and cancer diseases, advancements in imaging techniques, and expanding applications in theranostics.
According to the WHO, on a global scale, in 2023, cancer was responsible for around 10 million deaths, marking the significance of early and precise diagnostics. Medical radioisotopes, specifically Fluorine-18, which is primarily used in PET scans, enable the early detection of cancer. The growing demand for personalized treatment and efficient diagnostics drives the need for radioisotopes.
Moreover, advancements in hybrid imaging solutions, such as SPECT/CT and PET/CT, have enhanced diagnostic accuracy. These improvements broaden the applications and intensify the clinical utility of radioisotopes. As these solutions have become more accessible and affordable, the adoption of medical isotopes has continued to rise notably.
Furthermore, theranostics—the use of a single radioactive agent for both treatment and diagnosis—is gaining prominence. Isotopes like Actinium-225 and Lutetium-177 offer personalized therapy with fewer side effects. This dual-function method improves treatment efficacy and enhances patient outcomes.
Nevertheless, the global market is limited by the low shelf life of radioisotopes and the high cost of machinery and isotope production. Several medical radioisotopes are not durable, making timely production and distribution intricate. For example, Technetium-99m has a shelf life of just 6 hours. This time constraint restricts the global supply chain, mainly in remote and underdeveloped regions. Moreover, nuclear reactors and cyclotrons used in isotope production require significant capital investment.
Additionally, radiation safety measures and regulatory compliance further increase operational expenses. These financial barriers hinder new industry entrants and limit industry expansion in developing or low-income nations. However, the global medical radioisotopes industry is opportune for the transition to cyclotron-based isotope production and advancements in generator systems and cold kits.
As reactors become obsolete, cyclotron-based production is gaining prominence for isotopes like Gallium-68 and Fluorine-18. These systems offer more localized and safer production with minimal regulatory barriers. The adoption of cyclotrons improves regional independence and supply reliability.
Also, cold kits that enable onsite preparation of radiopharmaceuticals are gaining traction. Likewise, generators like Tc-99m.Mo-99 systems allow hospitals to extract isotopes as needed. These innovations increase isotope utility and decrease dependency on immediate deliveries.
Key Insights:
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global medical radioisotopes market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 8.10% over the forecast period (2025-2034)
- In terms of revenue, the global medical radioisotopes market size was valued at around USD 5.90 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 11.00 billion by 2034.
- The medical radioisotopes market is projected to grow significantly due to the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases, expanding applications in theranostics, and robust investments from the private sector and government.
- Based on type, the Tc-99m segment is expected to lead the market, while the iodine radioisotopes racks segment is expected to grow considerably.
- Based on application, the diagnosis is the largest segment, while the nuclear therapy segment is projected to witness substantial revenue growth over the forecast period.
- Based on end-user, the hospitals segment is expected to lead the market compared to the diagnostic centers segment.
- Based on region, North America is projected to dominate the global market during the estimated period, followed by Europe.
Medical Radioisotopes Market: Growth Drivers
Growth of therapeutic applications of radioisotopes drives market growth
Besides diagnostics, the therapeutic use of medical radioisotopes is gaining traction, especially in targeted radionuclide therapy (TRT). Isotopes like Actinium-225 and Lutetium-177 are being largely used to treat neuroendocrine tumors, prostate cancer, and bone metastases. This dual-use potential (diagnosis + treatment) is fueling the growth of the medical radioisotopes market.
Additionally, research into alpha-emitting isotopes, such as Actinium-225, is expanding. Fusion Pharmaceuticals commenced Phase II trials of its alpha-emitting radioconjugates for solid tumors in May 2025, a move that is expected to transform cancer therapy and increase demand in this segment.
Growing chronic disease burden and geriatric population spur market growth
The growing elderly population is associated with high cases of cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, and cancer, all of which are domains where radioisotopes are used. Chronic diseases now account for over 7 percent of global mortality, according to WHO data (2023), creating an urgent demand for effective diagnostics and treatment monitoring machinery. Radioisotopes offer painless, faster, and more accurate insights into disease progression and organ function.
For example, cardiac SPECT imaging using Technetium-99m is a commonly used nuclear imaging procedure in the geriatric population. Its use has expanded because of the rising burden of congestive heart failure and ischemic heart disease, mainly in developed nations like Germany, Japan, and the United States.
Medical Radioisotopes Market: Restraints
Aging production facilities and reactor shutdowns negatively impact market progress
A notable share of the global radioisotope supply relies on the aging nuclear reactors, the majority of which are nearing the end of their operational life cycle. Reactors like HFR in the Netherlands and NRU (shut down in 2018) in Canada have experienced repeated disturbances. The lack of universal reactor redundancy poses a significant barrier to maintaining a stable supply.
Europe experienced a 9% fall in isotope availability due to the lengthy maintenance shutdown of the Belgian BR2 reactor, one of the leading producers of Mo-99 on the continent.
Medical Radioisotopes Market: Opportunities
Integration of digital platforms and AI in nuclear imaging is an opportunity for the market progress
AI is transforming medical imaging by enabling faster image reconstruction, improving diagnostic accuracy, and providing personalized treatment recommendations based on nuclear scans. The incorporation of artificial intelligence in nuclear medicine presents an opportunity to enhance the clinical utility of radioisotopes, thereby impacting the growth of the medical radioisotopes industry.
Subtle Medical and Siemens Healthineers incorporated resolution-enhancement algorithms and AI-based noise reduction into PET/CT workflows, decreasing the scan period by 40% without compromising diagnostic quality.
Medical Radioisotopes Market: Challenges
Waste disposal and radioactive byproducts management restrict the growth of market
The production and application of radioisotopes in medicine generate radioactive waste, which should be managed under stringent safety and ecological standards. Disposing of isotopic waste, particularly long-lived isotopes, requires ongoing compliance and specialized infrastructure, as regulated by regulations governing nuclear waste disposal.
Economies like Japan and the United States are facing increased legal and public scrutiny regarding the establishment of new radioactive waste sites.
Germany's nuclear regulatory agency, BfS, has flagged issues with accumulated low-level radioactive waste at many university hospitals due to delays in federal acceptance for novel storage facilities.
Medical Radioisotopes Market: Report Scope
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Medical Radioisotopes Market |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 5.90 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 11.00 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 8.10% |
| Number of Pages | 213 |
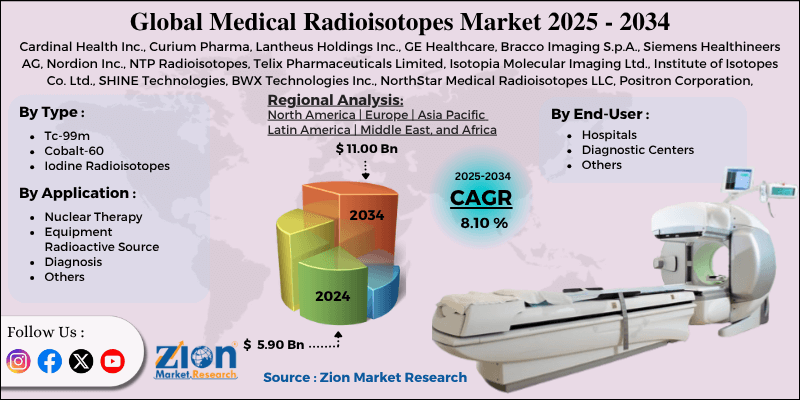
| Key Companies Covered | Cardinal Health Inc., Curium Pharma, Lantheus Holdings Inc., GE Healthcare, Bracco Imaging S.p.A., Siemens Healthineers AG, Nordion Inc., NTP Radioisotopes, Telix Pharmaceuticals Limited, Isotopia Molecular Imaging Ltd., Institute of Isotopes Co. Ltd., SHINE Technologies, BWX Technologies Inc., NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes LLC, Positron Corporation, and others. |
| Segments Covered | By Type, By Application, By End-User, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2025 - 2034 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Medical Radioisotopes Market: Segmentation
The global medical radioisotopes market is segmented based on type, application, end-user, and region.
Based on type, the global medical radioisotopes industry is divided into Tc-99m, Cobalt-60, and iodine radioisotopes. Tc-99m is the most widely used medical radioisotope, accounting for over 80% of all nuclear medicine procedures worldwide. It is primarily used in diagnostic imaging, particularly SPECT scans, due to its durability for up to 6 hours and its gamma-ray emission characteristics. The isotope is used for more than a million procedures yearly, globally, increasing its importance in nuclear diagnostic imaging.
Based on application, the global medical radioisotopes market is segmented into nuclear therapy, equipment radioactive source, diagnosis, and others. The Diagnosis segment captures a notable share of the market, accounting for 75% of the global market. Radioisotopes such as Fluorine-18, Iodine-123, and Technetium-99m are widely used in imaging procedures, including PET and SPECT, to detect various medical conditions. The increasing volume of diagnostic procedures, exceeding 40 million annually, fuels segmental dominance, particularly with the rising access to healthcare and the demand for non-invasive diagnostics.
Based on end-user, the global market is segmented into hospitals, diagnostic centers, and others. The 'hospitals' segment led the market in the past year and is expected to continue leading in the coming years, backed by its broad network, ability to perform both diagnostic imaging and therapeutic procedures with radioisotopes, and access to nuclear medicine departments. The incorporated nature of care from diagnosis to treatment, coupled with the growing hospital admissions for cardiac, cancer, and thyroid disorders, strengthens their dominance.
Medical Radioisotopes Market: Regional Analysis
North America to witness significant growth over the forecast period
North America is expected to continue leading the medical radioisotopes market due to high diagnostic volumes, advanced healthcare infrastructure, growing incidences of chronic diseases, and the increasing adoption of targeted radionuclide therapies. North America, particularly the U.S., has the most developed healthcare network, enabling the broader use of nuclear medicine procedures.
According to SNMMI, over 20 million nuclear medicine procedures are performed annually in the United States alone. This broad diagnostic activity drives the demand for radioisotopes like F-18 and Tc-99m, thereby strengthening the regional market's prominence. Also, the region witnesses heavy cases of cancer, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular diseases, major drivers for therapeutic radioisotopes and diagnostic usage.
For example, the ACS (American Cancer Society) predicted 2 million new cancer cases in the United States in 2024. The growing burden notably contributes to the stable demand for therapeutic (Lu-177, I-131) and diagnostic (Tc-99m) isotopes.
Moreover, North America leads in adopting advanced treatments like Actinium-255 therapies and Lutetium-177 DOTATATE, especially for prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors. With FDA approvals and reimbursement frameworks in place, the region experiences the speedy commercialization of theranostic applications, thereby expanding its demand in the radioisotope market.
Europe is the second-leading region in the medical radioisotopes industry, driven by the heavy use of nuclear medicine in member states, leadership in the supply of medical isotopes, and substantial R&D investment and capital expertise. Europe performs over 10 million nuclear medicine procedures yearly, with nations like France, Germany, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom being key contributors. These procedures are widely used for diagnosing cardiovascular diseases, cancers, and neurological disorders.
Europe's per-capita diagnostic rate withstands a strong demand for isotopes like Fluorine-18 and Technetium-99m. Europe is also a leader in medical isotope production facilities, comprising HFR in the Netherlands and the BR2 reactor in Belgium. The Netherlands alone supplies approximately 30% of the TC-99m globally. This production capacity notably contributes to the global supply, promising strategic relevance.
In addition, Europe is a center for advanced nuclear medicine research, with university hospitals, Euratom, and IAEA partner institutions fronting innovation in radiopharmaceuticals. EU-funded schemes, such as PRISMAP, emphasize the production of next-generation therapeutic isotopes. These efforts enhance the clinical translation of novel isotopes, such as Lutetium-177 and Actinium-225.
Medical Radioisotopes Market: Competitive Analysis
The global medical radioisotopes market profiles players like:
- Cardinal Health Inc.
- Curium Pharma
- Lantheus Holdings Inc.
- GE Healthcare
- Bracco Imaging S.p.A.
- Siemens Healthineers AG
- Nordion Inc.
- NTP Radioisotopes
- Telix Pharmaceuticals Limited
- Isotopia Molecular Imaging Ltd.
- Institute of Isotopes Co. Ltd.
- SHINE Technologies
- BWX Technologies Inc.
- NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes LLC
- Positron Corporation
Medical Radioisotopes Market: Key Market Trends
Growing demand for technetium-99m (Tc-99m) based diagnostics:
Technetium-99m continues to lead nuclear medicine procedures, accounting for nearly 80% of the worldwide radioisotope use. Its application in oncology, cardiology, and bone scans is growing because of its cost-effectiveness and short lifespan. The rising cardiovascular and cancer incidences are fueling its rising adoption on a global scale.
Inclination toward non-reactor-based radioisotope production:
There is a remarkable inclination towards accelerator-based and cyclotron-based production of isotopes, such as Iodine-123 and Tc-99m, fueled by concerns over radioactive waste and aging reactors. The United States, Canada, and Key parts of Europe are heavily investing in alternative production routes. This trend improves supply security while decreasing dependency on nuclear reactors.
The global medical radioisotopes market is segmented as follows:
By Type
- Tc-99m
- Cobalt-60
- Iodine Radioisotopes
By Application
- Nuclear Therapy
- Equipment Radioactive Source
- Diagnosis
- Others
By End-User
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Centers
- Others
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
Table Of Content
Methodology
FrequentlyAsked Questions
Medical radioisotopes are radioactive elements used in nuclear medicine for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases. They emit radiation that visualizes internal organs using imaging methods like SPECT and PET scans.
The global medical radioisotopes market is projected to grow due to the increasing demand for non-invasive diagnostics, advancements in imaging techniques, and extensive use in the diagnosis of endocrine and neurological disorders.
According to study, the global medical radioisotopes market size was worth around USD 5.90 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 11.00 billion by 2034.
The CAGR value of the medical radioisotopes market is expected to be approximately 8.10% from 2025 to 2034.
North America is expected to lead the global medical radioisotopes market during the forecast period.
The key players profiled in the global medical radioisotopes market include Cardinal Health, Inc., Curium Pharma, Lantheus Holdings, Inc., GE Healthcare, Bracco Imaging S.p.A., Siemens Healthineers AG, Nordion Inc., NTP Radioisotopes, Telix Pharmaceuticals Limited, Isotopia Molecular Imaging Ltd., Institute of Isotopes Co., Ltd., SHINE Technologies, BWX Technologies, Inc., NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes, LLC, and Positron Corporation.
The report examines key aspects of the medical radioisotopes market, including a detailed analysis of existing growth factors and restraints, as well as future growth opportunities and challenges that influence the market.
HappyClients
Zion Market Research
Tel: +1 (302) 444-0166
USA/Canada Toll Free No.+1 (855) 465-4651
3rd Floor,
Mrunal Paradise, Opp Maharaja Hotel,
Pimple Gurav, Pune 411061,
Maharashtra, India
Phone No +91 7768 006 007, +91 7768 006 008
US OFFICE NO +1 (302) 444-0166
US/CAN TOLL FREE +1 (855) 465-4651
Email: sales@zionmarketresearch.com
We have secured system to process your transaction.
Our support available to help you 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Monday - Friday: 9AM - 6PM
Saturday - Sunday: Closed