Low Carbon Building Market Size, Trend, Growth, Industry Analysis 2034

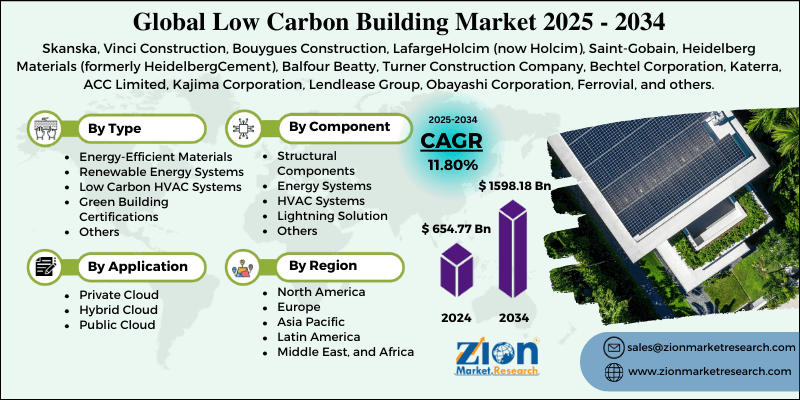
Low Carbon Building Market By Type (Energy-Efficient Materials, Renewable Energy Systems, Low Carbon HVAC Systems, Green Building Certifications, and Others), By Component (Structural Components Energy Systems, HVAC Systems, Lightning Solution, and Others), By Application (Commercial, Residential, Industrial), and By Region - Global and Regional Industry Overview, Market Intelligence, Comprehensive Analysis, Historical Data, and Forecasts 2025 - 2034
| Market Size in 2024 | Market Forecast in 2034 | CAGR (in %) | Base Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD 654.77 Billion | USD 1598.18 Billion | 11.80% | 2024 |
Low Carbon Building Market: Industry Perspective
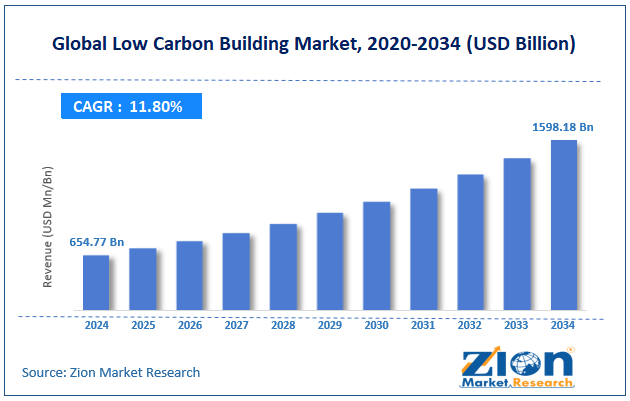
The global low carbon building market size was worth around USD 654.77 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 1598.18 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 11.80% between 2025 and 2034.
Low Carbon Building Market: Overview
Low-carbon building refers to the construction, design, and operation of buildings that reduce carbon emissions throughout their lifespan, from material sourcing to power use and waste management. These buildings focus on energy efficiency, sustainable materials, renewable energy integration, and innovative solutions to decrease GHG. The global low carbon building market is projected to witness substantial growth driven by growing environmental awareness, urbanization, population growth, and technological improvements in green construction. Consumers and businesses are primarily concerned about climate change. Businesses integrate ESG goals into their operations, while users prefer ecologically friendly buildings.
According to surveys, more than 60% of worldwide tenants prefer sustainability in property decisions, motivating developers to adopt low-carbon practices. Speedy urbanization, mainly in Africa and the Asia Pacific, fuels large-scale construction, offering opportunities to implement sustainable designs from the ground up. With the urban population anticipated to surpass 68% by 2050, sustainable urban infrastructure becomes a vital factor. Advancement in building materials, smart sensors, energy-efficient HVAC systems, and renewable energy solutions drives industry adoption. Low-emission concrete, solar-integrated designs, and energy-efficient glass reduce carbon footprint while enhancing building performance.
Although drivers exist, the global market is challenged by factors like the lack of skilled labor and low awareness in developing economies. Low-carbon adoption needs expertise in the construction, design, and operation of sustainable buildings. The lack of professional engineers, architects, and technicians may hamper the market growth. In the developing economies, a majority of stakeholders prioritize cost over sustainability. A lack of understanding of the long-term benefits of low-carbon buildings limits the industry penetration.
Even so, the global low-carbon building industry is well-positioned due to the integration of smart building technologies, the rise of green certifications, and corporate real estate demand. AI, IoT, and building automation systems enhance energy management, occupant comfort, and predictive maintenance, fueling the adoption of low-carbon solutions. The rising adoption of BREEAM, EDGE, LEED, and other certifications offers opportunities for consultants, developers, and service providers. Companies pursuing ESG and net-zero goals are fueling the demand for sustainable industrial and office spaces, building fresh avenues for technology providers and developers.
Key Insights:
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global low carbon building market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 11.80% over the forecast period (2025-2034)
- In terms of revenue, the global low carbon building market size was valued at around USD 654.77 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1598.18 billion by 2034.
- The low carbon building market is projected to grow significantly due to increasing demand for energy-efficient buildings, smart city development, and urbanization, as well as rising prices of traditional energy sources.
- Based on type, the energy-efficient materials segment is expected to lead the market, while the renewable energy systems segment is expected to grow considerably.
- Based on component, the structural components segment is the dominating segment, while the energy systems segment is projected to witness sizeable revenue over the forecast period.
- Based on the application, the commercial segment is expected to lead the market compared to the residential segment.
- Based on region, Europe is projected to dominate the global market during the estimated period, followed by the Asia Pacific.
Low Carbon Building Market: Growth Drivers
Expansion of green building certifications boosts the market growth
The proliferation of green building rating systems like WELL, BREEAM, and LEED has propelled the growth of the low-carbon building market by promoting sustainable construction practices. In 2024, the number of LEED-certified projects surged by 15% over the past year, with PAC experiencing speedy adoption.
Certification plays a key role as a quality benchmark, appealing to tenants and investors who value environmental responsibility. Corporate sustainability goals also comply with these certifications, fueling commercial demand. The growing recognition and credibility of green certifications across the globe incentivize developers to invest in low-carbon building technologies.
How is investment growth in sustainable infrastructure fueling the low carbon building market?
Investment in green and sustainable initiatives has increased worldwide, fueling demand and impacting the low carbon building market. Global green building investments hit $1.5 trillion in 2024, a 12% rise from 2023, denoting rising confidence among private and institutional investors. Financial institutions and ESG-focused capital are vastly preferring projects that reduce carbon footprints. Initiatives like the World Bank's Climate-Smart Building Program are offering funding for energy-efficient construction in developing regions. This financial support facilitates the large-scale deployment of low-carbon solutions, thereby increasing the sustainability of more viable buildings.
Low Carbon Building Market: Restraints
The scarcity of a skilled workforce negatively impacts the market progress
Implementing low-carbon construction requires trained professionals who are familiar with energy-efficient designs, sustainable material handling, and green certifications. Several regions lack specialized training programs, especially in the emerging economies, which hinders project execution. News reports from 2025 indicate that European developers are importing expertise to comply with green building standards. The lack of a skilled workforce remains a significant restraint on market development.
Low Carbon Building Market: Opportunities
How is the global low-carbon building market responsive to government subsidies and incentives for green construction?
The government is offering tax incentives, subsidies, and low-interest loans to encourage low-carbon construction. The EU's Renovation Wave initiative and the United States Inflation Reduction Act are a few instances of programs promoting energy-efficient retrofits and novel sustainable buildings.
In 2024, India announced extra incentives for green-certified residential and commercial projects. India introduced additional incentives for green-certified residential and commercial buildings in 2023, which positively impacted the growth of the low carbon building industry. These policies decrease financial hindrances, opening doors for large-scale adoption.
Low-Carbon Building Market: Challenges
How is the low carbon building market challenged by technological integration and compatibility issues?
Integrating novel technologies like building automation, smart energy systems, and renewable energy into traditional construction practices offers challenges. Deloitte's 2024 report found that nearly 35% of low-carbon projects experienced delays due to system integration complexities. In early 2025, a California commercial project experienced cost overruns while adopting AI-driven energy optimization. These technological difficulties hamper smooth adoption and increase risks.
Low Carbon Building Market: Report Scope
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Low Carbon Building Market |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 654.77 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 1598.18 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 11.80% |
| Number of Pages | 213 |
| Key Companies Covered | Skanska, Vinci Construction, Bouygues Construction, LafargeHolcim (now Holcim), Saint-Gobain, Heidelberg Materials (formerly HeidelbergCement), Balfour Beatty, Turner Construction Company, Bechtel Corporation, Katerra, ACC Limited, Kajima Corporation, Lendlease Group, Obayashi Corporation, Ferrovial, and others. |
| Segments Covered | By Type, By Component, By Application, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2025 - 2034 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Low Carbon Building Market: Segmentation
The global low carbon building market is segmented based on type, component, application, and region.
Based on type, the global low carbon building industry is divided into energy-efficient materials, renewable energy systems, low carbon HVAC systems, green building certifications, and others. The energy-efficient materials segment registered substantial growth in the market. These materials comprise low-emission concrete, sustainable flooring, high-performance insulation, and energy-efficient glass, which decrease energy consumption and curb operational costs. Homeowners and developers are largely adopting these materials to obey building codes and enhance overall building performance. The growing awareness of long-term energy savings and ecological impact is fueling strong growth for this segment globally.
Based on component, the global low carbon building market is segmented into structural components, energy systems, HVAC systems, lightning solutions, and others. The structural components segment held a leading market share. It comprises foundations, roofs, and floors built with ecological and low-carbon materials. These components are vital since they register for a larger share of a building's embodied carbon. Developers are actively using materials like low-emission concrete, recycled steel, and sustainably sourced timber to comply with environmental standards. Energy-efficient goals, regulatory compliance, and growing awareness of the ecological impact of construction materials drive their extensive adoption.
Based on application, the global market is segmented into commercial, residential, and industrial. The commercial segment holds leadership since these buildings have significant energy consumption because of HVAC systems, lighting, and equipment, making them prime candidates for energy-saving solutions. They comprise retail spaces, offices, and educational institutions, denoting a significant market share. Developers are increasingly adopting low-carbon materials, integrating renewable energy, and implementing smart energy systems to reduce operational costs and comply with regulatory standards. The growing focus on green certifications and ESG compliance among businesses also propels the adoption of low-carbon solutions in commercial places.
Low Carbon Building Market: Regional Analysis
Which factors enable Europe to hold a strong foothold in the global Low Carbon Building Market?
Europe is likely to sustain its leadership in the low carbon building market due to high adoption of green building certifications, emphasis on renewable energy integration, and high environmental awareness among corporates and consumers. European nations have broadly adopted green building certifications like DGNB, LEED, and BREEAM, making certified low-carbon benchmarks for sustainability and quality.
In 2023, more than 40% of new commercial constructions in the region were BREEAM-certified, denoting strong corporate and developer commitment to low carbon construction practices. Europe also leads in integrating renewable energy technologies into buildings, comprising geothermal systems, solar PV, and energy-efficient HVAC solutions.
For instance, economies like France and Germany reported renewable energy adoption in 55% of newly constructed commercial buildings in 2023, which significantly decreased operational carbon emissions. European corporations and consumers prioritize ESG goals and sustainability, motivating developers to adopt low-carbon practices. According to surveys, more than 60% of European tenants choose to stay in green-certified buildings, which surges industry demand and fuels the regional dominance.
Asia Pacific continues to secure the second-highest share in the low carbon building industry owing to speedy urbanization, growing environmental awareness and corporate ESG goals, and increasing adoption of smart technologies. Asia Pacific is witnessing the fastest rate of urbanization across the globe, creating strong demand for new commercial, residential, and industrial buildings.
By 2025, more than 2.7 billion individuals are anticipated to live in urban areas in the region, fueled by large-scale construction activities. This speedy growth offers opportunities to integrate low carbon designs and energy-saving technologies from the outset, propelling the industry adoption. Environmental consciousness among businesses and consumers is growing speedily in APAC. Corporations are integrating ESG targets in their operations, and tenants in smart cities are considering sustainability when choosing office and living spaces.
According to the surveys, nearly 50% of the commercial tenants in the region prefer eco-friendly buildings, boosting developers' investment in low-carbon solutions. The region is broadly integrating renewable energy systems, smart building technologies, and energy-efficient HVAC. Economies like South Korea, China, and India reported more than 40% of fresh industrial and commercial buildings in 2023, incorporating energy management systems or renewable energy, decreasing operational carbon emissions, and fueling market growth.
Low Carbon Building Market: Competitive Analysis
The prominent players in the global low carbon building market include:
- Skanska
- Vinci Construction
- Bouygues Construction
- LafargeHolcim (now Holcim)
- Saint-Gobain
- Heidelberg Materials (formerly HeidelbergCement)
- Balfour Beatty
- Turner Construction Company
- Bechtel Corporation
- Katerra
- ACC Limited
- Kajima Corporation
- Lendlease Group
- Obayashi Corporation
- Ferrovial
Low Carbon Building Market: Key Market Trends
Adoption of renewable energy systems:
Buildings are increasingly incorporating renewable energy solutions, such as wind turbines, rooftop solar panels, and geothermal systems. This trend is fueled by government incentives, declining costs of renewable solutions, and the move towards net-zero energy buildings, helping residential and commercial projects reduce their carbon footprint.
Use of low-carbon and sustainable materials:
There is a rising emphasis on ecologically-friendly construction materials, comprising low-emission concrete, sustainable insulation, recycled steel, and bamboo. Architects and developers prioritize these materials to decrease embodied carbon, obey green certifications, and comply with strict regulatory demands.
The global low carbon building market is segmented as follows:
By Type
- Energy-Efficient Materials
- Renewable Energy Systems
- Low Carbon HVAC Systems
- Green Building Certifications
- Others
By Component
- Structural Components
- Energy Systems
- HVAC Systems
- Lightning Solution
- Others
By Application
- Commercial
- Residential
- Industrial
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
Table Of Content
Methodology
FrequentlyAsked Questions
Low-carbon building refers to the construction, design, and operation of buildings that reduce carbon emissions throughout their lifespan, from material sourcing to power use and waste management. These buildings focus on energy efficiency, sustainable materials, renewable energy integration, and innovative solutions to decrease GHG.
The global low carbon building market is projected to grow due to growing government regulations on carbon emissions, advancements in green building materials, and corporate sustainability initiatives and ESG adoption.
According to study, the global low carbon building market size was worth around USD 654.77 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 1598.18 billion by 2034.
The CAGR value of the low carbon building market is expected to be around 11.80% during 2025-2034.
The low carbon building value chain includes design and construction, sustainable material production, operation/maintenance, and system installation, along with retrofitting services and certification.
Technological advancements, such as energy-efficient materials, smart building systems, and renewable energy integration, are reducing carbon emissions and advancing building performance. They enable predictive maintenance, real-time energy management, and optimized resource use, fueling market adoption.
Europe is expected to lead the global low carbon building market during the forecast period.
The key players profiled in the global low carbon building market include Skanska, Vinci Construction, Bouygues Construction, LafargeHolcim (now Holcim), Saint-Gobain, Heidelberg Materials (formerly HeidelbergCement), Balfour Beatty, Turner Construction Company, Bechtel Corporation, Katerra, ACC Limited, Kajima Corporation, Lendlease Group, Obayashi Corporation, and Ferrovial.
The competitive landscape of the low carbon building market is highly fragmented, with regional and global players offering smart systems, sustainable materials, and green construction solutions. Companies compete through certifications, innovation, strategic partnerships, and energy-efficient technologies to capture market share.
The report examines key aspects of the low carbon building market, including a detailed analysis of existing growth factors and restraints, as well as an examination of future growth opportunities and challenges that will impact the market.
HappyClients
Zion Market Research
Tel: +1 (302) 444-0166
USA/Canada Toll Free No.+1 (855) 465-4651
3rd Floor,
Mrunal Paradise, Opp Maharaja Hotel,
Pimple Gurav, Pune 411061,
Maharashtra, India
Phone No +91 7768 006 007, +91 7768 006 008
US OFFICE NO +1 (302) 444-0166
US/CAN TOLL FREE +1 (855) 465-4651
Email: sales@zionmarketresearch.com
We have secured system to process your transaction.
Our support available to help you 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Monday - Friday: 9AM - 6PM
Saturday - Sunday: Closed